List of destroyed landmarks in Spain: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[File:Palacio de los Alcañices1.jpg|120px]]|| [[Palacio de Alcañices|Palace of the Marquis of Alcañices]] || [[Madrid]], Community of Madrid || Herrerian || 17th century || 1883, during the during the ensanches/eixamples in the Spanish confiscation period || Demolished || It was ordered to built by Luis Méndez de Haro 6th Marquis del Carpio, a favorite of Philip IV. Subsequently was inhabited by the Dukes of Béjar, Pedro de Alcántara Téllez-Girón y Beaufort Spontin and Maria Josefa Pimentel, also by the 15th Marquess of Alcañices when began to be used with its gardens with parterres by the nobility as a rest area. Also was inhabited by the 16th Marquess of Alcañices who marriage to Russian Princess Sofia Sergeyevna Trubetskaya, in this time the palace became the center of the Alfonsine meetings. Had as visitors Isidro González Velázquez, Guesdon, Parcerisa, Clifford, Laurent, etc. In 1854 it built new stables at the palace. The cost of supporting the monarchy, from the Duke of Sesto, and the works of extension of the nearby streets forced the Duke of Sesto to sell the Palace in 1882 to the board of the Bank of Spain who it demolished |
|[[File:Palacio de los Alcañices1.jpg|120px]]|| [[Palacio de Alcañices|Palace of the Marquis of Alcañices]] || [[Madrid]], Community of Madrid || Herrerian || 17th century || 1883, during the during the ensanches/eixamples in the Spanish confiscation period || Demolished || It was ordered to built by Luis Méndez de Haro 6th Marquis del Carpio, a favorite of Philip IV. Subsequently was inhabited by the Dukes of Béjar, Pedro de Alcántara Téllez-Girón y Beaufort Spontin and Maria Josefa Pimentel, also by the 15th Marquess of Alcañices when began to be used with its gardens with parterres by the nobility as a rest area. Also was inhabited by the 16th Marquess of Alcañices who marriage to Russian Princess Sofia Sergeyevna Trubetskaya, in this time the palace became the center of the Alfonsine meetings. Had as visitors Isidro González Velázquez, Guesdon, Parcerisa, Clifford, Laurent, etc. In 1854 it built new stables at the palace. The cost of supporting the monarchy, from the Duke of Sesto, and the works of extension of the nearby streets forced the Duke of Sesto to sell the Palace in 1882 to the board of the Bank of Spain who it demolished |
||
|- |
|||
|[[File:Palacio de Indo.jpg|120px]]|| [[Palacio de Indo|Palace of Indo]] || [[Madrid]], Community of Madrid || Herrerian || 17th century || 1883, during the during the ensanches/eixamples in the Spanish confiscation period || Demolished || It was ordered to built by Luis Méndez de Haro 6th Marquis del Carpio, a favorite of Philip IV. Subsequently was inhabited by the Dukes of Béjar, Pedro de Alcántara Téllez-Girón y Beaufort Spontin and Maria Josefa Pimentel, also by the 15th Marquess of Alcañices when began to be used with its gardens with parterres by the nobility as a rest area. Also was inhabited by the 16th Marquess of Alcañices who marriage to Russian Princess Sofia Sergeyevna Trubetskaya, in this time the palace became the center of the Alfonsine meetings. Had as visitors Isidro González Velázquez, Guesdon, Parcerisa, Clifford, Laurent, etc. In 1854 it built new stables at the palace. The cost of supporting the monarchy, from the Duke of Sesto, and the works of extension of the nearby streets forced the Duke of Sesto to sell the Palace in 1882 to the board of the Bank of Spain who it demolished |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
Revision as of 02:52, 12 May 2016
This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: This page is very messy and contains many English language errors as well as many dead links. (March 2016) |
This list of missing landmarks in Spain includes remarkable buildings, castles, royal palaces, medieval towers, medieval walls and other remarkable built structures that no longer exist in Spain, also incldng in this article those that partially are still standing.
Existed hundred destroyed landmarks that were all over Spain, although still standing much wonders, many of these monuments could well be world heritage sites or be a proofs of the history of its cities in today. For a more complete list see the Category:Destroyed landmarks in Spain.
List (by alphabetical order)
| Image | Name | Location | Architectural style/era | Date of construction | Date of demolition / rebuilt | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File:Recreation of Archbishop's Palace of Alcalá before the 1939 fire.jpg | Archbishop's Palace of Alcalá de Henares | Alcalá de Henares, Community of Madrid | Mudéjar, Herrerian | 1209 | 1939, during the Spanish Civil War | Partially survived | It is the place where was performed the first meeting between the Catholic Monarchs and Christopher Columbus. It was barracks of tanks and ammunitions, both during and after the Spanish Civil War, when, for the failure to prevent flammable materials that were there there was a big fire. It was not the first suffered in its long history, but one of the most voracious, because it destroyed much of the buildings, however some survived |
| File:Old Spa Gran Hotel La Toja in 1907.jpg | Balneario da Toxa | Island of A Toxa, Galicia | Galician Regionalist of the time | 1907 | 1945, during the Francoist period | Almost complete refurbishment | Suffered a restoration, a almost complete refurbishment, although survives various sections or elements inside the modern building |
| Avinguda de la Llum | Barcelona, Catalonia | Modern | 1940 | 1992, during the modern government and autonomies | Partially survived | It was the first underground mall of its kind to open in Europe. It was partially demolished for the 1992 Summer Olympics. Now survives sections in a underground stage of a Sephora store | |
 |
Casa Trinxet | Barcelona, Catalonia | Modernisme | 1904 | 1968, during the Francoist period | Demolished | It was demolished despite attempts by artists and intellectuals to save it for conversion into a museum of Modernisme |
 |
Castle of Burgos | Burgos, Castile and León | Visigothic, Moorish, Christian | 1813, during the Napoleonic invasion | Ruins survived | It was a castle and alcázar, being inhabited by some Castilian kings. During the Napoleonic invasion the French soldiers transformated significanttly the castle, and then Frenchs without any apparent justification exploded the castle, more than two hundred French soldiers died in the blast, and a church also destroyed, that shakes the entire population | |
 |
Church of San Pedro Mártir | Calatayud, Aragon | Mudéjar | 1368 | 1856, during the Spanish confiscation period | demolished | After of its confiscation and its use as barracks, was demolished on the pretext that blocked traffic on the road proceedings of Madrid |
 |
Buen Retiro Palace | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Herrerian | 1640 | 1808, during the Napoleonic invasion | Partially survived | It was for periods Royal residence. During the Napoleonic invasion the French troops stationed in Madrid used the palace and its annexes as barracks. Powder kegs were stored in the gardens and a bunker was built for them, causing irreparable damage, although survives the Hall of the Kingdoms; the Casón del Buen Retiro being now an annex of the Museo del Prado; and the gardens that forms the Retiro Park |
 |
Casa del Tesoro | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Christian | 16th century | 19th century, during the Napoleonic invasion | Demolished | It was demolished by Joseph Bonaparte (brother of Napoleon) and today in its place is the Plaza de Oriente |
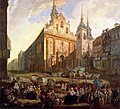 |
Churches of the Buen Suceso | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque | 1611, 1868 | 1854, 1975, during the ensanches/eixamples in the Spanish confisscation period and during the Francoist period | Demolished | The first church was also an hospital built by Juan de Herrera and ordered to built by Philip II of Spain. Due to the reform of the Puerta del Sol was demolished. Of this building remained a columns that were brought to the Casa de Bruguera, The Clock it wore the façade is the Clock of the Puerta del Sol; The second church it were given new tasks, such as the public and free consultation and cure and the relief in accidents on public roads, while assuming additional functions such as the special hospital for diseases of children and sick Home of Health for sick pensioners. In 1942, this second church it removed the hospital services, which become covered by the Directorate General of Health of the Army of the Air. It was demolished that then maybe threatens ruin |
 |
Convent of Copacabana | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque | 1620 | 1837, during the Spanish confiscation period | Demolished | It housed the image of the patron saint of Peru brought in 1662. In 1837 the monks were expelled and the convent disentailed during the Ecclesiastical confiscations of Mendizábal. It was the own Mendizábal who bought it at auction. Shortly after was shot down |
 |
Convent of San Felipe el Real | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque | 1547 | 1838, during the Spanish confiscation period | Demolished | It was a convent of Augustinian monks built by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, also it had a steps around the building which served as talking shop. It suffered a fire in 1718 and the whole complex was very mistreated during Napoleonic invasion. After the confiscation of Mendizábal, was demolished in 1838 to widen the Calle Mayor and, instead, was built the first apartment building in the city, the Casa Cordero |
 |
Convent of San Norberto | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque | 1611 | 1811, during the Napoleonic invasion | Demolished | It was victim of the king Joseph Bonaparte (brother of Napoleon) who it modified and and then he demolished it |
 |
Convent of San Norberto | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque | 1656 | 1872, during the Spanish confiscation period | Demolished | It was a Dominican convent made by the Churriguera family supported by the Count-Duke of Olivares. Also it had, in 19th century, a café shop established on the ground floor of the convent. Church and convent were secularized and confiscated in 1836, going to have many uses, from administrative center to headquarters Milicia Nacional. The complex entirely disappeared three years after suffering a strong fire |
 |
Gothic-Mudéjar church of Humanejos | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Gothic, Mudéjar | 14th century | 19th century, 1980, during the Spanish confiscation period and the modern government and autonomies | Demolished | It is also possible that it was built on a previous also Christian temple. The church became a meeting point for the many travelers passing. This accelerated its deterioration, although it is conceivable that was the subject of intense looting. Was finally completely demolished in the 1980s for rose the today Autovía A-42 |
 |
Fiesta Alegre fronton | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque Revival | 1892 | 1965, during the Francoist period | Demolished | Fistly it was a Basque pelota court, and later was a Basketball court hosting the Real Madrid Baloncesto |
 |
Hotel Florida | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Ecleptic | 1924 | 1964, during the Francoist period | Demolished | It was a marble hotel. Figures as Ernest Hemingway, Mijaíl Koltsov, John Dos Passos, Geoffrey Cox, Henry Buckley, Ksawery Pruszyński, Wiadomosci Literackie, O. D. Gallagher and Herbert L. Matthew stayed at it during the Spanish Civil War where wrote important plays and articles |
 |
Noviciado de la Compañía de Jesús | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Baroque | 1606 | 1964, during the Spanish confiscation period | Partially survived | The Jesuits were finally expelled of this church by the confiscations of Mendizábal. After being used as a barracks for military engineers, in 1843 the building became house the Complutense University. But was reformed, now survives the perimeter walls, used for building the auditorium of the university. Of the rest of the complex are preserved the spaces of the two ancient cloisters, converted into courtyards, around which the various offices and classrooms are distributed |
 |
Palace of the Marquis of Alcañices | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Herrerian | 17th century | 1883, during the during the ensanches/eixamples in the Spanish confiscation period | Demolished | It was ordered to built by Luis Méndez de Haro 6th Marquis del Carpio, a favorite of Philip IV. Subsequently was inhabited by the Dukes of Béjar, Pedro de Alcántara Téllez-Girón y Beaufort Spontin and Maria Josefa Pimentel, also by the 15th Marquess of Alcañices when began to be used with its gardens with parterres by the nobility as a rest area. Also was inhabited by the 16th Marquess of Alcañices who marriage to Russian Princess Sofia Sergeyevna Trubetskaya, in this time the palace became the center of the Alfonsine meetings. Had as visitors Isidro González Velázquez, Guesdon, Parcerisa, Clifford, Laurent, etc. In 1854 it built new stables at the palace. The cost of supporting the monarchy, from the Duke of Sesto, and the works of extension of the nearby streets forced the Duke of Sesto to sell the Palace in 1882 to the board of the Bank of Spain who it demolished |
 |
Palace of Indo | Madrid, Community of Madrid | Herrerian | 17th century | 1883, during the during the ensanches/eixamples in the Spanish confiscation period | Demolished | It was ordered to built by Luis Méndez de Haro 6th Marquis del Carpio, a favorite of Philip IV. Subsequently was inhabited by the Dukes of Béjar, Pedro de Alcántara Téllez-Girón y Beaufort Spontin and Maria Josefa Pimentel, also by the 15th Marquess of Alcañices when began to be used with its gardens with parterres by the nobility as a rest area. Also was inhabited by the 16th Marquess of Alcañices who marriage to Russian Princess Sofia Sergeyevna Trubetskaya, in this time the palace became the center of the Alfonsine meetings. Had as visitors Isidro González Velázquez, Guesdon, Parcerisa, Clifford, Laurent, etc. In 1854 it built new stables at the palace. The cost of supporting the monarchy, from the Duke of Sesto, and the works of extension of the nearby streets forced the Duke of Sesto to sell the Palace in 1882 to the board of the Bank of Spain who it demolished |
See also
- Spanish confiscation
- List of demolished landmarks in Madrid
- List of demolished landmarks in Valencia
- List of demolished landmarks in Seville
- Reconstruction (architecture)
- Project of Filippo Juvarra for the Royal Palace of Madrid
