Jimmy Carter: Difference between revisions
→Governor of Georgia: Rewriting |
→Honors and awards: Split content to List of honors and awards received by Jimmy Carter and summarized |
||
| Line 448: | Line 448: | ||
==Honors and awards== |
==Honors and awards== |
||
{{Main|List of honors and awards received by Jimmy Carter}} |
|||
[[File:Jimmy Carter with model of SSN-23.jpg|thumb|Former President and Navy submariner Jimmy Carter (left) hoists a replica of the [[USS Jimmy Carter (SSN-23)]] given to him by Secretary of the Navy John H. Dalton (right) at a naming ceremony in the Pentagon on April 28, 1998]] |
[[File:Jimmy Carter with model of SSN-23.jpg|thumb|Former President and Navy submariner Jimmy Carter (left) hoists a replica of the [[USS Jimmy Carter (SSN-23)]] given to him by Secretary of the Navy John H. Dalton (right) at a naming ceremony in the Pentagon on April 28, 1998]] |
||
[[File:FORPRES.jpg|right|thumb|4 U.S. Presidents. Former President Carter (right), walks with, from left, George H.W. Bush, George W. Bush and Bill Clinton during the dedication of the [[William J. Clinton Presidential Center and Park]] in [[Little Rock, Arkansas|Little Rock]], Arkansas on November 18, 2004]] |
[[File:FORPRES.jpg|right|thumb|4 U.S. Presidents. Former President Carter (right), walks with, from left, George H.W. Bush, George W. Bush and Bill Clinton during the dedication of the [[William J. Clinton Presidential Center and Park]] in [[Little Rock, Arkansas|Little Rock]], Arkansas on November 18, 2004]] |
||
[[File:Presidents Obama, Clinton, and Carter.jpg|thumb|right|Carter (right) with U.S. President [[Barack Obama]] (center) and former president Bill Clinton (left) on August 28, 2013.]] |
[[File:Presidents Obama, Clinton, and Carter.jpg|thumb|right|Carter (right) with U.S. President [[Barack Obama]] (center) and former president Bill Clinton (left) on August 28, 2013.]] |
||
Carter has received numerous awards and accolades since his presidency, and several institutions and locations have been named in his honor. His [[presidential library]], [[Jimmy Carter Library and Museum]] was opened in 1986.<ref>http://www.nytimes.com/1993/05/30/travel/carter-center-more-than-the-past.html?pagewanted=all</ref> In 1998, the US Navy named the third and [[USS Jimmy Carter (SSN-23)|last Seawolf-class submarine]] honoring former President Carter and his service as a submariner officer. It became one of the first US Navy vessels to be named for a person living at the time of naming.<ref>Jamie McIntyre, [http://www.cnn.com/US/9804/08/carter.sub/ "Navy to name submarine after former President Jimmy Carter"], CNN, April 8, 1998. Retrieved August 4, 2008.</ref> That year he also received the [[United Nations Prize in the Field of Human Rights|United Nations Human Rights Prize]], given in honor of human rights achievements,<ref>http://www.ohchr.org/EN/NewsEvents/Pages/HRPrizeListofpreviousrecipients.aspx</ref> and the [[Hoover Medal]], recognizing engineers who have contributed to global causes.<ref>https://www.asme.org/about-asme/get-involved/honors-awards/unit-awards/hoover-awards/1998</ref> He won the 2002 [[Nobel Peace Prize]],<ref>http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/2002/press.html</ref> which was partially a response to President [[George W. Bush]]'s [[Iraq War|threats of war against Iraq]] and Carter's criticism of the Bush administration.<ref>https://web.archive.org/web/20021016213347/http://www.cnn.com/2002/WORLD/europe/10/11/carter.nobel/index.html</ref> Six of Carter's audiobook recordings have been nominated for the [[Grammy Award for Best Spoken Word Album]]; his book ''[[Our Endangered Values]]'' won the award in 2007.<ref>http://dailycaller.com/2013/02/11/the-liberal-history-of-the-grammys-spoken-word-category/</ref><ref>http://www.nytimes.com/2007/02/12/arts/music/12gram.html?_r=0</ref> The Souther Field Airport in Americus was renamed Jimmy Carter Regional Airport in 2009.<ref>http://www.foxnews.com/politics/2009/10/11/jimmy-carter-regional-airport-reality/</ref> |
|||
Carter has received honorary degrees from many American and foreign colleges and universities. They include: |
|||
* [[Doctor of Laws|LL.D.]] (''[[Honorary degree|honoris causa]]'') [[Morehouse College]], 1972; [[Morris Brown College]], 1972; [[University of Notre Dame]], 1977; [[Emory University]], 1979; [[Kwansei Gakuin University]], 1981; [[Georgia Southwestern College]], 1981; [[New York Law School]], 1985; [[Bates College]], 1985; [[Centre College]], 1987; [[Creighton University]], 1987; [[University of Pennsylvania]], 1998 |
|||
* D.E. (''honoris causa'') [[Georgia Institute of Technology]], 1979 |
|||
* PhD (''honoris causa'') [[Weizmann Institute of Science]], 1980; [[Tel Aviv University]], 1983; [[University of Haifa]], 1987 |
|||
* [[Doctor of Humane Letters|D.H.L.]] (''honoris causa'') [[Commencement at CCSU|Central Connecticut State University]], 1985; [[Trinity College (Connecticut)|Trinity College]], 1998; [[Hoseo University]], 1998 |
|||
* [[Doctor (title)|Doctor]] (''honoris causa'') G.O.C. University, 1995; [[University of Juba]], 2002 |
|||
* [[Honorary Fellow]] of [[Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland]], 2007 |
|||
* Honorary Fellow of [[Mansfield College, Oxford]], 2007 |
|||
Among the honors Carter has received are the [[Presidential Medal of Freedom]] in 1999 and the [[Nobel Peace Prize]] in 2002. Others include: |
|||
* [[Freedom of the City]] of [[Newcastle upon Tyne]], England, 1977 |
|||
* [[Silver Buffalo Award]], [[Boy Scouts of America]], 1978 |
|||
* Gold medal, International Institute for Human Rights, 1979 |
|||
* International Mediation medal, [[American Arbitration Association]], 1979 |
|||
* [[Martin Luther King, Jr.]], Nonviolent Peace Prize, 1979 |
|||
* International Human Rights Award, Synagogue Council of America, 1979 |
|||
* Conservationist of the Year Award, 1979 |
|||
* [[Harry S. Truman]] Public Service Award, 1981 |
|||
* [[Ansel Adams]] Conservation Award, Wilderness Society, 1982 |
|||
* Human Rights Award, International League of Human Rights, 1983 |
|||
* World Methodist Peace Award, 1985 |
|||
* [[Albert Schweitzer]] Prize for Humanitarianism, 1987 |
|||
* Edwin C. Whitehead Award, National Center for Health Education, 1989 |
|||
* S. Roger Horchow Award for Greatest Public Service by a Private Citizen, [[Jefferson Awards for Public Service|Jefferson Awards]], 1990<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.jeffersonawards.org/pastwinners/national |title=National Winners | public service awards |publisher=Jefferson Awards.org |accessdate=November 29, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Liberty Medal]], [[National Constitution Center]], 1990 |
|||
* Spirit of America Award, National Council for the Social Studies, 1990 |
|||
* Physicians for Social Responsibility Award, 1991 |
|||
* [[Aristotle]] Prize, Alexander S. Onassis Foundation, 1991 |
|||
* [[W. Averell Harriman]] Democracy Award, National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, 1992 |
|||
* Spark M. Matsunaga Medal of Peace, US Institute of Peace, 1993 |
|||
* Humanitarian Award, CARE International, 1993 |
|||
* Conservationist of the Year Medal, National Wildlife Federation, 1993 |
|||
* Audubon Medal, [[National Audubon Society]], 1994<ref>{{cite web|url=http://articles.orlandosentinel.com/1994-11-14/news/9411140121_1_national-audubon-society-audubon-medal-carter |title=Former President Carter Awarded Audubon Medal - Orlando Sentinel |publisher=Articles.orlandosentinel.com |date=November 14, 1994 |accessdate=March 19, 2014}}</ref> |
|||
* Rotary Award for World Understanding, 1994 |
|||
* [[J. William Fulbright]] Prize for International Understanding, 1994 |
|||
* National Civil Rights Museum Freedom Award, 1994 |
|||
* UNESCO Félix Houphouët-Boigny Peace Prize, 1994 |
|||
* Great Cross of the Order of Vasco Nunéz de Balboa, Panama, 1995 |
|||
* Bishop John T. Walker Distinguished Humanitarian Award, Africare, 1996 |
|||
* Humanitarian of the Year, GQ Awards, 1996 |
|||
* Kiwanis International Humanitarian Award, 1996 |
|||
* [[Indira Gandhi]] Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development, 1997 |
|||
* Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter Awards for Humanitarian Contributions to the Health of Humankind, National Foundation for Infectious Diseases, 1997 |
|||
* [[United Nations Prize in the Field of Human Rights|United Nations Human Rights Award]], 1998 |
|||
* The [[Hoover Medal]], 1998 |
|||
* The [[Delta Prize for Global Understanding]], [[Delta Air Lines]] & The [[University of Georgia]], 1999 |
|||
* International Child Survival Award, UNICEF Atlanta, 1999 |
|||
* William Penn Mott, Jr., Park Leadership Award, National Parks Conservation Association, 2000<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.npca.org/annualdinner/past_awardees.html#mott |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110725210138/http://www.npca.org/annualdinner/past_awardees.html|archivedate=July 25, 2011| title=Salute to the Parks Awards: Past Awardees | publisher=[[National Parks Conservation Association]] | accessdate=June 14, 2010}}</ref> |
|||
* Zayed International Prize for the Environment, 2001 |
|||
* Jonathan M. Daniels Humanitarian Award, VMI, 2001 |
|||
* Herbert Hoover Humanitarian Award, [[Boys & Girls Clubs of America]], 2001 |
|||
* [[Christopher Award]], 2002 |
|||
* [[Grammy Award for Best Spoken Word Album]], National Academy of Recording Arts and Sciences, 2007<ref>Presidents who have won Grammies | [http://www.upvenue.com/music-news/blog-headline/1020/grammy-winning-presidents-and-candidates.html UpVenue].</ref> |
|||
* Berkeley Medal, [[University of California]] campus, May 2, 2007 |
|||
* International Award for Excellence and Creativity, [[Palestinian Authority]], 2009<ref>David Lev, [http://www.israelnationalnews.com/News/News.aspx/131843 "Gush Etzion Residents: Keep Carter out of our Town"], Arutz Sheva, June 14, 2009.</ref> |
|||
* Mahatma Gandhi Global Nonviolence Award, Mahatma Gandhi Center for Global Nonviolence, [[James Madison University]] (shared with his wife, Rosalynn Carter) |
|||
* Recipient of 2009 [[American Peace Award]] along with Rosalynn Carter<ref>{{cite web|url=http://americanpeaceaward.org/recipient09.html |title=The American Peace Award |publisher=The American Peace Award |accessdate=June 8, 2010}}</ref> |
|||
* International [[Catalonia]] Award 2010 |
|||
* International Advocate for Peace award by the [[Cardozo Journal of Conflict Resolution]] at [[Benjamin N. Cardozo School of Law|Cardozo School of Law]], April 10, 2013 |
|||
In 1998, the US Navy named the third and [[USS Jimmy Carter (SSN-23)|last Seawolf-class submarine]] honoring former President Carter and his service as a submariner officer. It became one of the first US Navy vessels to be named for a person living at the time of naming.<ref>Jamie McIntyre, [http://www.cnn.com/US/9804/08/carter.sub/ "Navy to name submarine after former President Jimmy Carter"], CNN, April 8, 1998. Retrieved August 4, 2008.</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 22:14, 13 July 2014
Jimmy Carter | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 39th President of the United States | |
| In office January 20, 1977 – January 20, 1981 | |
| Vice President | Walter Mondale |
| Preceded by | Gerald Ford |
| Succeeded by | Ronald Reagan |
| 76th Governor of Georgia | |
| In office January 12, 1971 – January 14, 1975 | |
| Lieutenant | Lester Maddox |
| Preceded by | Lester Maddox |
| Succeeded by | George Busbee |
| Member of the Georgia Senate from the 14th district | |
| In office January 14, 1963 – January 10, 1967 | |
| Preceded by | Constituency established |
| Succeeded by | Hugh Carter |
| Constituency | Sumter County |
| Personal details | |
| Born | James Earl Carter, Jr. October 1, 1924 Plains, Georgia, U.S. |
| Political party | Democratic Party |
| Spouse(s) | Eleanor Rosalynn Smith (m. 1946–present) |
| Relations |
|
| Children |
|
| Parent(s) | James Earl Carter, Sr. Bessie Lillian Gordy |
| Alma mater | |
| Profession | |
| Awards | Nobel Peace Prize Grand Cross of the Order of the Crown |
| Signature |  |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch/service | |
| Years of service | 1943–1953 |
| Rank | |
James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician and member of the Democratic Party who served as the 39th President of the United States from 1977 to 1981 and was awarded the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office. Before he became President, Carter served as a U.S. Naval officer, was a peanut farmer, served two terms as a Georgia State Senator and one as the Governor of Georgia, from 1971 to 1975.[2]
During Carter's term as President, he created two new cabinet-level departments: the Department of Energy and the Department of Education. He established a national energy policy that included conservation, price control, and new technology. In foreign affairs, Carter pursued the Camp David Accords, the Panama Canal Treaties, the second round of Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT II), and returned the Panama Canal Zone to Panama. He took office during a period of international stagnation and inflation, which persisted throughout his term. The end of his presidential tenure was marked by the 1979–1981 Iran hostage crisis, the 1979 energy crisis, the Three Mile Island nuclear accident, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, the United States boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow (the only U.S. boycott in Olympic history), and the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in Washington state.
By 1980, Carter's popularity had eroded. He survived a primary challenge from Ted Kennedy for the Democratic Party nomination in the 1980 election, but lost the general election to Ronald Reagan, the Republican candidate. On January 20, 1981, minutes after Carter's term in office ended, the 52 U.S. captives held at the U.S. embassy in Iran were released, ending the 444-day Iran hostage crisis.[3]
Carter and his wife Rosalynn founded the Carter Center in 1982,[4] a nongovernmental, not-for-profit organization that works to advance human rights. He has traveled extensively to conduct peace negotiations, observe elections, and advance disease prevention and eradication in developing nations. Carter is a key figure in the Habitat for Humanity project,[5] and also remains particularly vocal on the Israeli–Palestinian conflict.
Early life

James Earl Carter, Jr., was born October 1, 1924 at the Wise Sanatorium in Plains, Georgia.[note 1] He is a descendant of English settler Thomas Carter, who emigrated to Virginia in 1635. Several generations of Carters lived as cotton farmers in Georgia. Established in Sumter County, Plains was a small boomtown of 600 people when Carter was born. James Earl Carter, Sr., was a successful local businessman who ran a general store and had begun to invest in farmland. He had been a reserve second lieutenant in the U.S. Army's Quartermaster Corps during World War I. Carter's mother Bessie Lillian Gordy was a nurse at the Wise hospital. Carter was the first of Earl and Lillian's children; they moved several times in his infancy.[6]
The Carters settled on a dirt road in nearby Archery, which was almost entirely populated by impoverished African American families. They eventually had three more children: Gloria, Ruth, and Billy. Carter got along well with his parents, although his mother worked long hours and was often absent in his childhood. While Earl was staunchly pro-segregation, he allowed his son to befriend the black farmhands' children. An enterprising teenager, Carter was given his own acre of Earl's farmland where he grew, packaged and sold peanuts. He also rented out a section of tenant housing he had purchased.[6]
Carter attended the Plains High School from 1930, first grade, to 1941. The Great Depression was by then taking a toll on Archery and Plains, but the family benefited from New Deal farming subsidies and Earl took a position as a community leader. Carter was a diligent student with a fondness for reading.[note 2] His teacher Julia Coleman was a particular influence on him. As an adolescent he played on the Plains High basketball team; he joined the Future Farmers of America and developed his long-held interest in woodworking.[7]
Naval career
Though he had long dreamed of attending the U.S. Naval Academy in Annapolis, Carter had to wait for a sponsorship to match the cost. Meanwhile he enrolled at Georgia Southwestern College in nearby Americus. After taking additional mathematics courses at Georgia Tech, he was finally admitted to the Naval Academy in 1943. With his short, slim stature, Carter barely met the minimum physical requirements for entry. He was a good student but was seen as reserved and quiet, in contrast with the academy's aggressive hazing culture. While at the academy he fell for Ruth's friend Rosalynn Smith, whom he would marry shortly after graduation in 1946.[8] Carter graduated 59th out of 820 midshipmen, by his own recollection. Now based in Schenectady, New York, he served on surface ships and on diesel-electric submarines in the Atlantic and Pacific fleets. Promoted to a full lieutenant, he completed qualification for command of a diesel-electric submarine. He applied for the US Navy's fledgling nuclear submarine program run by then Captain Hyman G. Rickover, which he began in late 1952. Rickover's demands on his men and machines were legendary, and Carter later said that, next to his parents, Rickover had the greatest influence on him.[9]
On December 12, 1952, an accident with the experimental NRX reactor at Atomic Energy of Canada's Chalk River Laboratories caused a partial meltdown. The resulting explosion caused millions of liters of radioactive water to flood the reactor building's basement, and the reactor's core was no longer usable.[10] Carter was ordered to Chalk River, joining other American and Canadian service personnel. He was the officer in charge of the U.S. team assisting in the shutdown of the Chalk River Nuclear Reactor.[11] The painstaking process required each team member, including Carter, to don protective gear, and be lowered individually into the reactor to disassembly it for minutes at a time. During and after his presidency, Carter indicated that his experience at Chalk River shaped his views on nuclear power and nuclear weapons, including his decision not to pursue completion of the neutron bomb.[12]
Carter attended graduate school at Union College in 1952, majoring in reactor technology and nuclear physics until his resignation the following year.[13][14] Upon the death of his father in July 1953, Carter was urgently needed to run the family business, but he was torn over the decision. Staying in Schenectady he had the promise of a distinguished naval career, with eventual promotion to admiral a possibility. Furthermore, Rosalynn had grown comfortable with her family life and her husband's relative prestige; returning to the small-town life of Plains felt like a "monumental step backward" for her. On the other hand, Carter felt restricted by the military culture and yearned to take a path more like his father's. Resigning his commission, he was honorably discharged from the Navy on October 9, 1953.[15][16]
Farming
Earl Carter died a relatively wealthy man, recently elected to the Georgia House of Representatives. However, between his forgiveness of debts and the division of his wealth among heirs, his son inherited comparatively little. For a year, due to a limited real estate market, Jimmy, Rosalynn, and their three sons lived in public housing in Plains; Carter is the only U.S. president to have lived in housing subsidized for the poor. Knowledgeable in scientific and technological subjects, Carter took over the family peanut farm. The transition was difficult, as the harvest his first year failed due to drought and Carter was forced to open several lines of credit to keep the farm afloat. Carter took classes and read up on agriculture while Rosalynn learned accounting to manage the business' financials. Though they barely broke even the first year, Carter managed over the following years to expand and become quite successful.[17][18]
Early political career
State Senate
Racial tension was inflamed in Plains by the 1954 U.S. Supreme Court's anti-segregation ruling in Brown v. Board of Education. Carter was in favor of racial tolerance and integration—at one point, the local White Citizens' Council boycotted his peanut warehouse when he refused to join them—but he often kept those feelings to himself to avoid making enemies. By 1961 he was a prominent member of the community and the Baptist Church as well as chairman of the Sumter County school board, where he began to speak more loudly in favor of school integregation.[19] A state Senate seat was opened by the dissolution of Georgia's County Unit System in 1962; Carter announced his run for the seat 15 days before the election. Rosalynn, who had an instinct for politics and organization, was instrumental to his campaign. The initial results showed Carter losing, but this was the result of fraudulent voting orchestrated by Joe Hurst, the sheriff of Quitman County. Carter challenged the results; when fraud was confirmed, a new election was held, which he won.[20]
The Civil Rights Movement was well underway as Carter took office. He and his family had become staunch John F. Kennedy supporters. In 1962, the town of Americus was the site of mass beatings and incarcerations of black protesters, echoing similar unrest throughout the country. Carter remained relatively quiet on the issue at first, even as it polarized much of the county, to avoid alienating his segregationist colleagues. He did speak up on a few divisive issues, giving speeches against literacy tests and against a change to the Georgia Constitution which, he felt, implied a compulsion to practice religion.[21] A diligent legislator, Carter took speed-reading courses to keep up with the workload. Within two years his connections landed him on the state Democratic Executive Committee, where he helped rewrite the state party's rules. He became chairman of the West Central Georgia Planning and Development Commission, which oversaw the disbursement of federal and state grants for projects such as historic site restoration. When Bo Callaway was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in November 1964, Carter immediately began planning unseat him. The two had previously clashed over which two-year college would be expanded to a four-year college program by the state; Carter wanted it to go to Georgia Southwestern College in Americus, but Callaway wanted the funding to go to downtown Columbus. Carter saw Callaway, a Republican, as a rival who represented the inherited wealth and selfishness he despised in politics.[22]
Carter was re-elected in 1964 to serve a second two-year term. For a time in the State Senate, he chaired its Education Committee; he also sat on the Appropriations Committee toward the end of his second term. Before his term ended he contributed to a bill expanding statewide education funding and getting Georgia Southwestern a four-year program. He leveraged his regional planning work, giving speeches around the district to make himself more visible to potential voters. The last day of the term, March 3, 1966, he announced his run for Congress.[23]
Campaigns for governor
The congressional race was shaken up in mid-May when Callaway dropped out and decided to run for Governor of Georgia instead. Callaway was a very strong candidate, and state Democrats panicked over the prospect of losing the governorship they had held since Reconstruction. Carter soon decided to follow Callaway and run for governor himself. In the Democratic primary he ran as a moderate alternative to both the liberal former governor Ellis Arnall and the conservative Lester Maddox. In a press conference he described his ideology as "Conservative, moderate, liberal and middle-of-the-road. ... I believe I am a more complicated person than that."[24] He lost the Democratic primary, but drew enough votes as a third-place candidate to force Arnall into a runoff election with Maddox. A chain of events then resulted in Maddox, the dark horse candidate, being elected governor.[note 3] The result was a sharp blow to Carter, who was left deeply in debt. His attempt to rescue the race from Callaway had resulted in the unlikely election of the segregationist Maddox, which he considered an even worse outcome.[25]
Carter returned to his agriculture business and, during the next four years, carefully planned his next campaign for Governor in 1970. This period was a spiritual turning point for Carter; he grew increasingly evangelical, undertaking several religious missions in other states. Inspired by his sister Ruth and liberal theologians such as Reinhold Niebuhr, he declared himself born again, a growing movement in 1960s America. His last child Amy was born around this time.[26][27]
The liberal former governor, Carl Sanders, was Carter's main opponent in the 1970 Democratic primary. Carter ran a more modern campaign than his last, employing printed graphics and statistical analysis. Responding to poll data, Carter leaned more conservative than before. He positioned himself as a populist, quickly going negative against Sanders for his wealth (labeling him "Cufflinks Carl") and associating him with the national Democratic Party. He accused Sanders of corruption, but when pressed by the media, could come up with no evidence.[28][29] Throughout the campaign Carter sought both the black vote and the "Wallace vote", after the prominent segregationist George Wallace. While he met with black figures such as Martin Luther King, Sr. and Andrew Young, and visited many black-owned businesses, he also praised Wallace and promised to invite him to give a speech in Georgia. He implied support or dislike of private schools depending on the audience. The appeal to racism became more blatant over time; Carter's senior campaign aides handed out a photograph of his opponent Sanders celebrating with black basketball players.[28][29]
That September, Carter came ahead of Sanders in the first ballot by 49 to 38 percent, leading to a runoff. The campaign grew even more bitter; Carter's campaign criticized Sanders for supporting Martin Luther King, Jr. Carter won the runoff election with 60 percent of the vote—winning 7 percent of the black vote—and went on to win the general election easily over the Republican Hal Suit, a local news anchor. Once he was elected, Carter began to speak confidently against Georgia's racist politics. Leroy Johnson, a black state Senator, voiced his support for Carter, saying, "I understand why he ran that kind of ultra-conservative campaign. ... I don't believe you can win this state without being a racist."[28]
Governor of Georgia
Carter was sworn in as the 76th Governor of Georgia on January 12, 1971. He declared in his inaugural speech that "the time of racial segregation was over. No poor, rural, weak, or black person should ever again have to bear the additional burden of being deprived of the opportunity for an education, a job, or simple justice." The crowd was reportedly shocked by this message, contrasting starkly with Georgia's political culture and particularly Carter's campaign. The many segregationists who had supported Carter during the race felt betrayed. Time magazine ran a story on the progressive "New South" governors elected that year in a May 1971 issue, featuring a cover illustration of Carter.[30][31][32]
Lester Maddox, Carter's predecessor as governor, became lieutenant governor. Carter had endorsed Maddox, although the two did not campaign as a ticket. The two found little common ground during their four years of service, often publicly feuding with each other.[33] Richard Russell, Jr., then President pro tempore of the United States Senate, died in office during Carter's second week in office; the newly inaugurated governor appointed David H. Gambrell, state Democratic Party chair, to fill Russell's unexpired term in the Senate.[34]
With Carter's reluctance to engage in back-slapping and political favors, the legislature found him frustrating to work with.[35][36] He looked to aggressively expand the governor's authority while reducing the complexity of the state government. Therefore he negotiated a bill allowing him to propose executive restructuring and to force a vote on it. He implemented zero-based budgeting within state departments and added a Judicial Selection Commission to verify the credentials of judges appointed by the governor.[35] The reorganization plan was submitted in January 1972, but had a cool reception in the legislature. After two weeks of negotiations it was passed at midnight on the last day of the session.[37] Ultimately he merged about 300 state agencies into 30—a fact he would emphasize in his presidential run—although it is disputed that there were any overall cost savings from doing so.
Civil rights were a heartfelt priority for Carter. He expanded the number of black state employees, judges, and board members. He hired Rita Jackson Samuels, a black woman, to advise him on potential appointments.[38] He placed portraits of Martin Luther King, Jr., and two other prominent black Georgians in the capitol building, even as the Ku Klux Klan picketed the unveiling ceremony.[39] Still, Carter tried to keep his conservative allies comfortable. He co-sponsored an anti-busing resolution with George Wallace at the 1971 National Governors Conference.[38] After the U.S. Supreme Court threw out Georgia's death penalty statute in Furman v. Georgia (1972), Carter signed a revised death penalty statute which addressed the court's objections, thus re-introducing the practice in the state. Carter later regretted endorsing the death penalty, saying, "I didn't see the injustice of it as I do now."[40]
Carter pushed reforms through the legislature to provide equal state aid to schools in the wealthy and poor areas of Georgia, set up community centers for mentally handicapped children, and increase educational programs for convicts. Carter took pride in his program for the appointment of judges and state government officials. Under this program, all such appointments were based on merit, rather than political influence.[41][42]
In one of his more controversial decisions,[43] he vetoed a plan to build a dam on Georgia's Flint River. After surveying the river and the literature himself, he argued that the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers was underestimating both the project's cost and its impact on the region. The veto won the attention of environmentalists nationwide.[39] When Lieutenant William Calley was convicted in a military trial and sentenced to life for his role in the My Lai Massacre in South Vietnam, a politically polarizing issue, Carter avoided paying direct tribute to Calley. He instead instituted "American Fighting Man's Day" and asked Georgians to drive for a week with their lights on in support of the military.[44]
National ambition
Looking toward a potential presidential run, Carter engaged himself in national politics and public appearances. He was named to several southern planning commissions and was a delegate to the 1972 Democratic National Convention, where the liberal U.S. Senator George McGovern was the likely presidential nominee. Carter tried to ingratiate himself with the conservative, anti-McGovern voters, so that the convention would consider him for McGovern's running mate on a compromise ticket. He endorsed Senator Henry "Scoop" Jackson, in part to distance himself from George Wallace. Carter was still fairly obscure at the time, and his attempt at triangulation failed; the 1972 Democratic ticket went to McGovern and Senator Thomas Eagleton.[45]
After McGovern's loss in November 1972, Carter began meeting regularly with his fledgling campaign staff. He had quietly decided to begin putting a presidential bid together. He tried unsuccessfully to become chairman of the National Governors Association to boost his visibility. On David Rockefeller's endorsement he was named to the Trilateral Commission in April 1973. The following year he was named chairman of the Democratic National Committee's congressional, as well as gubernatorial, campaigns.[46] That year he appeared as the first guest on an episode of the game show What's My Line, signing in as "X", to hide his occupation. After his job was identified on question seven of ten by Gene Shalit, he talked about having brought movie production to the state of Georgia, citing Deliverance, and the then-unreleased The Longest Yard.
1976 presidential campaign
When Carter entered the Democratic Party presidential primaries in 1976, he was considered to have little chance against nationally better-known politicians. His name recognition was two percent. When he told his family of the decision to run for president, his mother asked, "President of what?"[citation needed] As the Watergate scandal of President Nixon was still fresh in the voters' minds, Carter's position as an outsider, distant from Washington, D.C., became an asset. He promoted government reorganization. Carter published Why Not the Best? in June 1976 to help introduce himself to the American public.[47]

Carter became the front-runner early on by winning the Iowa caucuses and the New Hampshire primary. He used a two-prong strategy: In the South, which most had tacitly conceded to Alabama's George Wallace, Carter ran as a moderate favorite son. When Wallace proved to be a spent force, Carter swept the region. In the North, Carter appealed largely to conservative Christian and rural voters; he had little chance of winning a majority in most states. He won several Northern states by building the largest single bloc. Carter's strategy involved reaching a region before another candidate could extend influence there. He had traveled over 50,000 miles, visited 37 states, and delivered over 200 speeches before any other candidates announced that they were in the race.[48] Initially dismissed as a regional candidate, Carter proved to be the only Democrat with a truly national strategy, and he clinched the nomination.
The national news media discovered and promoted Carter, as Lawrence Shoup noted in his 1980 book The Carter Presidency and Beyond:
What Carter had that his opponents did not was the acceptance and support of elite sectors of the mass communications media. It was their favorable coverage of Carter and his campaign that gave him an edge, propelling him rocket-like to the top of the opinion polls. This helped Carter win key primary election victories, enabling him to rise from an obscure public figure to President-elect in the short space of 9 months.
Carter was interviewed by Robert Scheer of Playboy for the November 1976 issue, which hit the newsstands a couple of weeks before the election. While discussing his religion's view of pride, Carter said: "I've looked on a lot of women with lust. I've committed adultery in my heart many times."[49] He is the only American president to have been interviewed by Playboy.
As late as January 26, 1976, Carter was the first choice of only four percent of Democratic voters, according to a Gallup poll. Yet "by mid-March 1976 Carter was not only far ahead of the active contenders for the Democratic presidential nomination, he also led President Ford by a few percentage points", according to Shoup.[50]
He chose Senator Walter F. Mondale as his running mate. He attacked Washington in his speeches, and offered a religious salve for the nation's wounds.[51]
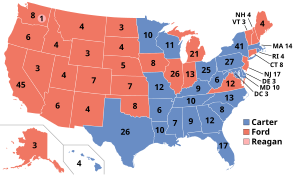
Carter began the race with a sizable lead over Ford, who narrowed the gap during the campaign, but lost to Carter in a narrow defeat on November 2, 1976. Carter won the popular vote by 50.1 percent to 48.0 percent for Ford, and received 297 electoral votes to Ford's 240. Carter became the first contender from the Deep South to be elected President since the 1848 election. Carter carried fewer states than Ford—23 states to the defeated Ford's 27—yet Carter won with the largest percentage of the popular vote (50.1 percent) of any non-incumbent since Dwight Eisenhower.
Presidency
Carter's tenure was a time of continuing inflation and recession, as well as an energy crisis. On January 7, 1980, Carter signed Law H.R. 5860 aka Public Law 96-185 known as The Chrysler Corporation Loan Guarantee Act of 1979, bailing out Chrysler Corporation. He cancelled military pay raises during a time of high inflation and government deficits.
Carter attempted to calm various conflicts around the world, most visibly in the Middle East with the signing of the Camp David Accords; giving back the Panama Canal; and signing the SALT II nuclear arms reduction treaty with Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev. His final year was marred by the Iran hostage crisis, which contributed to his losing the 1980 election to Ronald Reagan.
U.S. energy crisis

On April 18, 1977, Carter delivered a televised speech declaring that the U.S. energy crisis during the 1970s was the moral equivalent of war. He encouraged energy conservation by all U.S. citizens and installed solar water heating panels on the White House.[52][53] He wore sweaters to offset turning down the heat in the White House.

EPA Love Canal Superfund
In 1978, Carter declared a federal emergency in the neighborhood of Love Canal in the city of Niagara Falls, New York. More than 800 families were evacuated from the neighborhood, which was built on top of a toxic waste landfill. The Superfund law was created in response to the situation. Federal disaster money was appropriated to demolish the approximately 500 houses, the 99th Street School, and the 93rd Street School, which were built on top of the dump; and to remediate the dump and construct a containment area for the hazardous wastes. This was the first time that such a process had been undertaken. Carter acknowledged that several more "Love Canals" existed across the country, and that discovering such hazardous dumpsites was "one of the grimmest discoveries of our modern era".
Deregulation

In 1977, Carter appointed Alfred E. Kahn, a professor of economics at Cornell University, to be chair of the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB). He was part of a push for deregulation of the industry, supported by leading economists, leading 'think tanks' in Washington, a civil society coalition advocating the reform (patterned on a coalition earlier developed for the truck-and-rail-reform efforts), the head of the regulatory agency, Senate leadership, the Carter administration, and even some in the airline industry. This coalition swiftly gained legislative results in 1978.
The Airline Deregulation Act (Pub. L. 95–504) was signed into law by President Carter on October 24, 1978. The main purpose of the act was to remove government control over fares, routes and market entry (of new airlines) from commercial aviation. The Civil Aeronautics Board's powers of regulation were to be phased out, eventually allowing market forces to determine routes and fares. The Act did not remove or diminish the FAA's regulatory powers over all aspects of airline safety.
In 1979, Carter deregulated the American beer industry by making it legal to sell malt, hops, and yeast to American home brewers for the first time since the effective 1920 beginning of Prohibition in the United States.[54] This deregulation led to an increase in home brewing over the 1980s and 1990s that by the 2000s had developed into a strong craft microbrew culture in the United States, with over 2,000 breweries and brewpubs in the United States by 2012.[55][56]
U.S. boycott of the Moscow Olympics
In response to the 1979 Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, Carter decided to boycott the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow, which raised a bitter controversy. It was the only time since the founding of the modern Olympics in 1896 that the United States had not participated in a Summer or Winter Olympics. The Soviet Union retaliated by boycotting the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. It did not withdraw troops from Afghanistan until 1989 (eight years after Carter left office).
1980 presidential campaign
Carter later wrote that the most intense and mounting opposition to his policies came from the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, which he attributed to Ted Kennedy's ambition to replace him as president.[57] Kennedy surprised his supporters by running a weak campaign, and Carter won most of the primaries and secured renomination. However, Kennedy had mobilized the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, which gave Carter weak support in the fall election.[58]
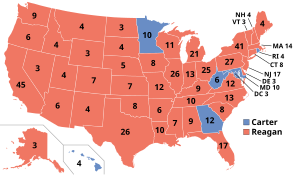
Carter's campaign for re-election in 1980 was one of the most difficult, and least successful, in history. He faced strong challenges from the right (Republican Ronald Reagan), the center (independent John B. Anderson), and the left (Democrat Ted Kennedy). He had to run against his own "stagflation"-ridden economy, while the hostage crisis in Iran dominated the news every week. He alienated liberal college students, who were expected to be his base, by re-instating registration for the military draft. His campaign manager and former appointments secretary, Timothy Kraft, stepped down some five weeks before the general election amid what turned out to have been an uncorroborated allegation of cocaine use.[59] Carter was defeated by Ronald Reagan in a landslide, and the Senate went Republican for the first time since 1952.
Public image

The Independent writes, "Carter is widely considered a better man than he was a president."[60] While he began his term with a 66 percent approval rating,[61] this had dropped to 34 percent approval by the time he left office, with 55 percent disapproving.[62]
In the wake of Nixon's Watergate Scandal, exit polls from the 1976 Presidential election suggested that many still held Gerald Ford's pardon of Nixon against him.[63] By comparison Carter seemed a sincere, honest, and well-meaning Southerner.[60]
His administration suffered from his inexperience in politics. Carter paid too much attention to detail. He frequently backed down from confrontation and was quick to retreat when attacked by political rivals. He appeared to be indecisive and ineffective, and did not define his priorities clearly. He seemed to be distrustful and uninterested in working with other groups, or even with Congress when controlled by his own party, as well as fellow Democratic senators which he denounced for being controlled by special interest groups.[64] Though he made efforts to address many of these issues in 1978, the approval he won from his reforms did not last long.
In the 1980 campaign, Ronald Reagan projected an easy self-confidence, in contrast to Carter's serious and introspective temperament. Carter's personal attention to detail, his pessimistic attitude, his seeming indecisiveness and weakness with people were accentuated in contrast to Reagan's charismatic charm and delegation of tasks to subordinates.[64][65] Reagan used the economic problems, Iran hostage crisis, and lack of Washington cooperation to portray Carter as a weak and ineffectual leader. Carter was the first elected president since Hoover in 1932 to lose a reelection bid.
In the years since then, his reputation has much improved. Carter's presidential approval rating, at 31 percent just prior to the 1980 election, was polled in early 2009 at 64 percent.[66] His post-Presidency activities have been favorably received. Carter believes that George H. W. Bush, who actively sought him out and was far more courteous and interested in his advice than Reagan, contributed to the rise in his reputation.[60]
Post-presidency

In 1981, Carter returned to Georgia to his peanut farm, which he had placed into a blind trust during his presidency to avoid even the appearance of a conflict of interest. He found that the trustees had mismanaged the trust, leaving him more than one million dollars in debt. In the years that followed, he has led an active life, establishing the Carter Center, building his presidential library, teaching at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, and writing numerous books.[51] He has also contributed to the expansion of Habitat for Humanity, to build affordable housing. As of September 8, 2012, Carter has lived longer after leaving the White House than any other U.S. President.
Legacy as president
- Carter's presidency was initially viewed by most as a failure.[67][68][69] In historical rankings of US presidents, the Carter presidency has ranged from No. 19 to #34.
- Although his presidency received mixed reviews, his peace keeping and humanitarian efforts since he left office have made Carter renowned as one of the most successful ex-presidents in US history.[70][71]
- The documentary Back Door Channels: The Price of Peace (2009) credits Carter's efforts at Camp David, which brought peace between Israel and Egypt, with bringing the only meaningful peace to the Middle East. The film opened the 2009 Monte-Carlo Television Festival in an invitation-only royal screening[72] on June 7, 2009 at the Grimaldi Forum in the presence of Albert II, Prince of Monaco.[73]
Carter Center and Nobel Prize

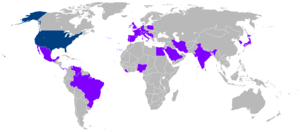
Carter has been involved in a variety of national and international public policy, conflict resolution, human rights and charitable causes. In 1982, he established The Carter Center in Atlanta to advance human rights and alleviate human suffering. The non-profit, nongovernmental Center promotes democracy, mediates and prevents conflicts, and monitors the electoral process in support of free and fair elections. It also works to improve global health through the control and eradication of diseases such as Guinea worm disease, river blindness, malaria, trachoma, lymphatic filariasis, and schistosomiasis. It also works to diminish the stigma of mental illnesses and improve nutrition through increased crop production in Africa.
A major accomplishment of The Carter Center has been the elimination of more than 99 percent of cases of Guinea worm disease, from an estimated 3.5 million cases in 1986 to 148 reported cases in 2013.[74] The Carter Center has monitored 96 elections in 38 countries since 1989.[75] It has worked to resolve conflicts in Haiti, Bosnia, Ethiopia, North Korea, Sudan and other countries. Carter and the Center support human rights defenders around the world and have intervened with heads of state on their behalf.
In 2002, President Carter received the Nobel Peace Prize for his work "to find peaceful solutions to international conflicts, to advance democracy and human rights, and to promote economic and social development" through The Carter Center.[76] Three sitting presidents, Theodore Roosevelt, Woodrow Wilson and Barack Obama, have received the prize; Carter is unique in receiving the award for his actions after leaving the presidency. He is, along with Martin Luther King, Jr., one of only two native Georgians to receive the Nobel.
Diplomacy
North Korea
In 1994, North Korea had expelled investigators from the International Atomic Energy Agency and was threatening to begin processing spent nuclear fuel. In response, then-President Clinton pressured for US sanctions and ordered large amounts of troops and vehicles into the area to brace for war.
Bill Clinton secretly recruited Carter to undertake a peace mission to North Korea,[77] under the guise that it was a private mission of Carter's. Clinton saw Carter as a way to let North Korean President Kim Il-sung back down without losing face.[78]
Carter negotiated an understanding with Kim Il-sung, but went further and outlined a treaty, which he announced on CNN without the permission of the Clinton White House as a way to force the US into action. The Clinton Administration signed a later version of the Agreed Framework, under which North Korea agreed to freeze and ultimately dismantle its current nuclear program and comply with its nonproliferation obligations in exchange for oil deliveries, the construction of two light water reactors to replace its graphite reactors, and discussions for eventual diplomatic relations.
The agreement was widely hailed at the time as a significant diplomatic achievement.[79][80] In December 2002, the Agreed Framework collapsed as a result of a dispute between the George W. Bush Administration and the North Korean government of Kim Jong-il. In 2001, Bush had taken a confrontational position toward North Korea and, in January 2002, named it as part of an "Axis of Evil". Meanwhile, North Korea began developing the capability to enrich uranium. Bush Administration opponents of the Agreed Framework believed that the North Korean government never intended to give up a nuclear weapons program, but supporters believed that the agreement could have been successful and was undermined.[81]
In August 2010, Carter traveled to North Korea in an attempt to secure the release of Aijalon Mahli Gomes. Gomes, a U.S. citizen, was sentenced to eight years of hard labor after being found guilty of illegally entering North Korea. Carter successfully secured the release.[82]
Middle East
Carter and experts from The Carter Center assisted unofficial Israeli and Palestinian negotiators in designing a model agreement for peace–-called the Geneva Accord–-in 2002–2003.[83]
Carter has also in recent years become a frequent critic of Israel's policies in Lebanon, the West Bank, and Gaza.[84][85]
In 2006, at the UK Hay Festival, Carter stated that Israel has at least 150 nuclear weapons. He expressed his support for Israel as a country, but criticized its domestic and foreign policy; "One of the greatest human rights crimes on earth is the starvation and imprisonment of 1.6m Palestinians," said Carter.
He mentioned statistics showing nutritional intake of some Palestinian children was below that of the children of Sub-Saharan Africa and described the European position on Israel as "supine".[86]
In April 2008, the London-based Arabic newspaper Al-Hayat reported that Carter met with exiled Hamas leader Khaled Mashaal on his visit to Syria. The Carter Center initially did not confirm nor deny the story. The US State Department considers Hamas a terrorist organization.[87] Within this Mid-East trip, Carter also laid a wreath on the grave of Yasser Arafat in Ramallah on April 14, 2008.[88] Carter said on April 23 that neither Condoleezza Rice nor anyone else in the State Department had warned him against meeting with Hamas leaders during his trip.[89] Carter spoke to Mashaal on several matters, including "formulas for prisoner exchange to obtain the release of Corporal Shalit."[90]
In May 2007, while arguing that the United States should directly talk to Iran, Carter again stated that Israel has 150 nuclear weapons in its arsenal.[91]
In December 2008, Carter visited Damascus again, where he met with Syrian President Bashar Assad, and the Hamas leadership. During his visit he gave an exclusive interview to Forward Magazine, the first ever interview for any American president, current or former, with a Syrian media outlet.[92][93]
Carter visited with three officials from Hamas who have been living at the International Red Cross office in Jerusalem since July 2010. Israel believes that these three Hamas legislators had a role in the 2006 kidnapping of Israeli soldier Gilad Shalit, and has a deportation order set for them.[94]
Africa
Carter held summits in Egypt and Tunisia in 1995–1996 to address violence in the Great Lakes region of Africa.[95]
Carter played a key role in negotiation of the Nairobi Agreement in 1999 between Sudan and Uganda.[96]
On June 18, 2007, Carter, accompanied by his wife, arrived in Dublin, Ireland, for talks with President Mary McAleese and Bertie Ahern concerning human rights. On June 19, Carter attended and spoke at the annual Human Rights Forum at Croke Park. An agreement between Irish Aid and The Carter Center was also signed on this day.
Americas
Carter led a mission to Haiti in 1994 with Senator Sam Nunn and former chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Colin Powell to avert a US-led multinational invasion and restore to power Haiti's democratically elected president, Jean-Bertrand Aristide.[97]
Carter visited Cuba in May 2002 and had full discussions with Fidel Castro and the Cuban government. He was allowed to address the Cuban public uncensored on national television and radio with a speech that he wrote and presented in Spanish. In the speech, he called on the US to end "an ineffective 43-year-old economic embargo" and on Castro to hold free elections, improve human rights, and allow greater civil liberties.[98] He met with political dissidents; visited the AIDS sanitarium, a medical school, a biotech facility, an agricultural production cooperative, and a school for disabled children; and threw a pitch for an all-star baseball game in Havana. The visit made Carter the first President of the United States, in or out of office, to visit the island since the Cuban revolution of 1959.[99]
Carter observed the Venezuela recall elections on August 15, 2004. European Union observers had declined to participate, saying too many restrictions were put on them by the Hugo Chávez administration.[100] A record number of voters turned out to defeat the recall attempt with a 59 percent "no" vote.[101] The Carter Center stated that the process "suffered from numerous irregularities," but said it did not observe or receive "evidence of fraud that would have changed the outcome of the vote".[102] On the afternoon of August 16, 2004, the day after the vote, Carter and Organization of American States (OAS) Secretary General César Gaviria gave a joint press conference in which they endorsed the preliminary results announced by the National Electoral Council. The monitors' findings "coincided with the partial returns announced today by the National Elections Council," said Carter, while Gaviria added that the OAS electoral observation mission's members had "found no element of fraud in the process." Directing his remarks at opposition figures who made claims of "widespread fraud" in the voting, Carter called on all Venezuelans to "accept the results and work together for the future".[103] A Penn, Schoen & Berland Associates (PSB) exit poll had predicted that Chávez would lose by 20 percent; when the election results showed him to have won by 20 percent, Douglas Schoen commented, "I think it was a massive fraud".[104] US News & World Report offered an analysis of the polls, indicating "very good reason to believe that the [Penn, Schoen & Berland] exit poll had the result right, and that Chávez's election officials – and Carter and the American media – got it wrong." The exit poll and the Venezuela government's control of election machines became the basis of claims of election fraud. However an Associated Press report states that Penn, Schoen & Berland used volunteers from pro-recall organization Súmate for fieldwork, and its results contradicted five other opposition exit polls.[105]
Following Ecuador's severing of ties with Colombia in March 2008, Carter brokered a deal for agreement between the countries' respective presidents on the restoration of low-level diplomatic relations announced June 8, 2008.[106][107]
Vietnam
On November 18, 2009, Carter visited Vietnam to build houses for the poor. The one-week program, known as Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter Work Project 2009, built 32 houses in Dong Xa village, in the northern province of Hải Dương. The project launch was scheduled for November 14, according to the news source which quoted the Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokeswoman Nguyen Phuong Nga. Administered by the non-governmental and non-profit Habitat for Humanity International (HFHI), the annual program of 2009 would build and repair 166 homes in Vietnam and some other Asian countries with the support of nearly 3,000 volunteers around the world, the organization said on its website. HFHI has worked in Vietnam since 2001 to provide low-cost housing, water, and sanitation solutions for the poor. It has worked in provinces like Tiền Giang and Đồng Nai as well as Ho Chi Minh City.[108]
The Elders
On July 18, 2007, Carter joined Nelson Mandela in Johannesburg, South Africa, to announce his participation in The Elders, a group of independent global leaders who work together on peace and human rights issues.[109] The Elders work globally, on thematic as well as geographically specific subjects. The organization's priority issue areas include the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Korean Peninsula, Sudan and South Sudan, sustainable development, and equality for girls and women.[110]
Carter has been actively involved in the work of The Elders, participating in visits to Cyprus, the Korean Peninsula, and the Middle East, among others[111] In October 2007, Carter toured Darfur with several of the Elders, including Desmond Tutu. Sudanese security prevented him from visiting a Darfuri tribal leader, leading to a heated exchange.[112] He returned to Sudan with fellow Elder Lakhdar Brahimi in May 2012 as part of The Elders’ efforts to encourage the presidents of Sudan and South Sudan to return to negotiations, and highlight the impact of the conflict on civilians.[113][114]
In November 2008, President Carter, former UN Secretary General Kofi Annan, and Graça Machel, wife of Nelson Mandela, were stopped from entering Zimbabwe, to inspect the human rights situation, by President Robert Mugabe's government. The Elders instead made their assessment from South Africa, meeting with Zimbabwe- and South Africa-based leaders from politics, business, international organisations and civil society in Johannesburg.[115]
Criticism of U.S. policy
In 2001, Carter criticized President Bill Clinton's controversial pardon of Marc Rich, calling it "disgraceful" and suggesting that Rich's financial contributions to the Democratic Party were a factor in Clinton's action.[116]
Carter has also criticized the presidency of George W. Bush and the Iraq War. In a 2003 op-ed in The New York Times, Carter warned against the consequences of a war in Iraq and urged restraint in use of military force.[117] In March 2004, Carter condemned George W. Bush and Tony Blair for waging an unnecessary war "based upon lies and misinterpretations" to oust Saddam Hussein. In August 2006, Carter criticized Blair for being "subservient" to the Bush administration and accused Blair of giving unquestioning support to Bush's Iraq policies.[118] In a May 2007 interview with the Arkansas Democrat-Gazette, he said, "I think as far as the adverse impact on the nation around the world, this administration has been the worst in history," when it comes to foreign affairs.[119][120] Two days after the quote was published, Carter told NBC's Today that the "worst in history" comment was "careless or misinterpreted," and that he "wasn't comparing this administration with other administrations back through history, but just with President Nixon's."[121] The day after the "worst in history" comment was published, White House spokesman Tony Fratto said that Carter had become "increasingly irrelevant with these kinds of comments."[122]
On May 19, 2007, Mr. Blair made his final visit to Iraq before stepping down as British Prime Minister, and Carter criticized him afterward. Carter told the BBC that Blair was "apparently subservient" to Bush and criticized him for his "blind support" for the Iraq war.[123] Carter described Blair's actions as "abominable" and stated that the British Prime Minister's "almost undeviating support for the ill-advised policies of President Bush in Iraq have been a major tragedy for the world." Carter said he believes that had Blair distanced himself from the Bush administration during the run-up to the invasion of Iraq in 2003, it might have made a crucial difference to American political and public opinion, and consequently the invasion might not have gone ahead. Carter states that "one of the defenses of the Bush administration ... has been, okay, we must be more correct in our actions than the world thinks because Great Britain is backing us. So I think the combination of Bush and Blair giving their support to this tragedy in Iraq has strengthened the effort and has made the opposition less effective, and prolonged the war and increased the tragedy that has resulted." Carter expressed his hope that Blair's successor, Gordon Brown, would be "less enthusiastic" about Bush's Iraq policy.[123]
In June 2005, Carter urged the closing of the Guantanamo Bay Prison in Cuba, which has been a focal point for recent claims of prisoner abuse.[124]
In September 2006, Carter was interviewed on the BBC's current affairs program Newsnight, voicing his concern at the increasing influence of the Religious Right on US politics.[125]
Due to his status as former President, Carter was a superdelegate to the 2008 Democratic National Convention. Carter announced his endorsement of Senator (now president) Barack Obama.
Speaking to the Syrian English monthly Forward Magazine of Syria, Carter was asked to give one word that came to mind when mentioning President George W. Bush. His answer was: the end of a very disappointing administration. His reaction to mentioning Barack Obama was: honesty, intelligence, and politically adept.[126][127]
In September 2009, Carter put weight behind allegations by Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez, pertaining to United States involvement in the 2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt by a civilian-military junta, saying that Washington knew about the coup and may have taken part.[128]
On June 16, 2011, the 40th anniversary of Richard Nixon's official declaration of America's War on Drugs, Carter wrote an op-ed in The New York Times urging the United States and the rest of the world to "Call Off the Global War on Drugs",[129] explicitly endorsing the initiative released by the Global Commission on Drug Policy earlier that month and quoting a message he gave to Congress in 1977 saying that "[p]enalties against possession of a drug should not be more damaging to an individual than the use of the drug itself."
Criticisms of President Obama
Carter has criticized the Obama administration for its use of drone strikes against suspected terrorists. Carter also said that he disagrees with President Obama's decision to keep the Guantánamo Bay detention camp open, saying that the inmates "have been tortured by waterboarding more than 100 times or intimidated with semiautomatic weapons, power drills or threats to sexually assault their mothers." He claimed that the U.S. government had no moral leadership, and was committing human rights violations, and is no longer "the global champion of human rights".[130]
In July 2013, Carter expressed his criticism of current federal surveillance programs as disclosed by Edward Snowden indicating that "America has no functioning democracy at this moment."[131][132]
Author

Carter has been a prolific author in his post-presidency, writing 21 of his 23 books. Among these is one he co-wrote with his wife, Rosalynn, and a children's book illustrated by his daughter, Amy. They cover a variety of topics, including humanitarian work, aging, religion, human rights, and poetry.
Palestine: Peace Not Apartheid
In a 2007 speech to Brandeis University, Carter stated: "I have spent a great deal of my adult life trying to bring peace to Israel and its neighbors, based on justice and righteousness for the Palestinians. These are the underlying purposes of my new book."[133]
In his book Palestine: Peace Not Apartheid, published in November 2006, Carter states:
Israel's continued control and colonization of Palestinian land have been the primary obstacles to a comprehensive peace agreement in the Holy Land.[134]
He declares that Israel's current policies in the Palestinian territories constitute "a system of apartheid, with two peoples occupying the same land, but completely separated from each other, with Israelis totally dominant and suppressing violence by depriving Palestinians of their basic human rights."[134] In an Op-Ed titled "Speaking Frankly about Israel and Palestine," published in the Los Angeles Times and other newspapers, Carter states:
The ultimate purpose of my book is to present facts about the Middle East that are largely unknown in America, to precipitate discussion and to help restart peace talks (now absent for six years) that can lead to permanent peace for Israel and its neighbors. Another hope is that Jews and other Americans who share this same goal might be motivated to express their views, even publicly, and perhaps in concert. I would be glad to help with that effort.[135]
While some – such as a former Special Rapporteur for both the United Nations Commission on Human Rights and the International Law Commission, as well as a member of the Israeli Knesset – have praised Carter for speaking frankly about Palestinians in Israeli occupied lands, others – including the envoy to the Middle East under Clinton, as well as the first director of the Carter Center[136][137] – have accused him of anti-Israeli bias. Specifically, these critics have alleged significant factual errors, omissions and misstatements in the book.[138][139]
The 2007 documentary film, Man from Plains, follows President Carter during his tour for the controversial book and other humanitarian efforts.[140]
In December 2009, Carter apologized for any words or deeds that may have upset the Jewish community in an open letter meant to improve an often tense relationship. He said he was offering an Al Het, a prayer said on Yom Kippur, the Jewish Day of Atonement.[141]
Involvement with Bank of Credit and Commerce International
After Carter left the presidency, his interest in the developing countries led him to having a close relationship with Agha Hasan Abedi, the founder of Bank of Credit and Commerce International (BCCI). Abedi was a Pakistani, whose bank had offices and business in a large number of developing countries. He was introduced to Carter in 1982 by Bert Lance, one of Carter's closest friends. (Unknown to Carter, BCCI had secretly purchased an interest in 1978 in National Bank of Georgia, which had previously been run by Lance and had made loans to Carter's peanut business.) Abedi made generous donations to the Carter Center and the Global 2000 Project. Abedi also traveled with Carter to at least seven countries in connection with Carter's charitable activities. The main purpose of Abedi's association with Carter was not charitable activities, but to enhance BCCI's influence, in order to open more offices and develop more business. In 1991, BCCI was seized by regulators, amid allegations of criminal activities, including illegally having control of several U.S. banks. Just prior to the seizure, Carter began to disassociate himself from Abedi and the bank.[142]
2012 Presidential race
Despite being a Democrat, Carter endorsed former Massachusetts governor Mitt Romney in the Republican party 2012 Presidential primary in mid-September 2011, not because he supported Romney, but because he felt Obama's re-election bid would be strengthened in a race against Romney.[143] Carter added that he thought Mitt Romney would lose in a match up against Obama and that he supported the president's re-election.[144]
Carter addressed the Democratic National Convention in North Carolina by videotape, and did not attend the convention in person.[145]
Other activities

Carter has participated in many ceremonial events such as the opening of his own presidential library and those of Presidents Ronald Reagan, George H. W. Bush, and Bill Clinton. He has also participated in many forums, lectures, panels, funerals and other events. Carter delivered a eulogy at the funeral of Coretta Scott King and, most recently, at the funeral of his former political rival, but later his close, personal friend and diplomatic collaborator, Gerald Ford.
President Jimmy Carter serves as an Honorary Chair for the World Justice Project.[146] The World Justice Project works to lead a global, multidisciplinary effort to strengthen the Rule of Law for the development of communities of opportunity and equity.[147]
Carter serves as Honorary Chair for the Continuity of Government Commission (he was co-chair with Gerald Ford until the latter's death). The Commission recommends improvements to continuity of government measures for the federal government.
Personal views
Abortion
Although "personally opposed" to abortion, after the landmark US Supreme Court decision Roe v. Wade, 410 US 113 (1973), Carter supported legalized abortion.[148] As president, he did not support increased federal funding for abortion services. He was criticized by the American Civil Liberties Union for not doing enough to find alternatives.[149]
In March 2012, during an interview on The Laura Ingraham Show, Carter expressed his view that the Democratic Party should be more pro-life. He said that it had been difficult for him, given his strong beliefs, to uphold Roe v. Wade while he was president.[150] In a March 29, 2012 interview with Laura Ingraham, Carter expressed his current view of abortion and his wish to see the Democratic Party becoming more pro-life: "I never have believed that Jesus Christ would approve of abortions and that was one of the problems I had when I was president having to uphold Roe v. Wade and I did everything I could to minimize the need for abortions. I made it easy to adopt children for instance who were unwanted and also initiated the program called Women and Infant Children or WIC program that's still in existence now. But except for the times when a mother's life is in danger or when a pregnancy is caused by rape or incest I would certainly not or never have approved of any abortions. I've signed a public letter calling for the Democratic Party at the next convention to espouse my position on abortion which is to minimize the need, requirement for abortion and limit it only to women whose life [sic?] are in danger or who are pregnant as a result of rape or incest. I think if the Democratic Party would adopt that policy that would be acceptable to a lot of people who are now estranged from our party because of the abortion issue."[151]
Death penalty
During his presidential campaigns, he expressed his opposition to the death penalty, as had George McGovern. Two successive nominees, Walter Mondale and Michael Dukakis, also opposed the death penalty.[152] Carter is known for his strong opposition to the death penalty; in his Nobel Prize lecture, he urged "prohibition of the death penalty".[153] Carter continued to speak out against the death penalty in the US and abroad.
In a letter to the Governor of New Mexico, Bill Richardson, Carter urged the governor to sign a bill to eliminate the death penalty and institute life in prison without parole instead. New Mexico abolished the death penalty in 2009. Carter wrote: "As you know, the United States is one of the few countries, along with nations such as Saudi Arabia, China, and Cuba, which still carry out the death penalty despite the ongoing tragedy of wrongful conviction and gross racial and class-based disparities that make impossible the fair implementation of this ultimate punishment."[154] In 2012, Carter wrote an op-ed in the LA Times supporting passage of a state referendum which would have ended the death penalty. He opened the article: "The process for administering the death penalty in the United States is broken beyond repair, and it is time to choose a more effective and moral alternative. California voters will have the opportunity to do this on election day."[155]
Carter has also called for commutations of death sentences for many death-row inmates, including Brian K. Baldwin (executed in 1999 in Alabama),[156] Kenneth Foster (sentence in Texas commuted in 2007)[157][158] and Troy Anthony Davis (executed in Georgia in 2011).[159]
Equality for women
In October 2000, Carter, a third-generation Southern Baptist, announced that he was severing ties to the Southern Baptist Convention over its opposition to women as pastors. What led Carter to take this action was a doctrinal statement by the Convention, adopted in June 2000, advocating a literal interpretation of the Bible. This statement followed a position of the Convention two years previously advocating the submission of wives to their husbands. Carter described the reason for his decision as due to: "an increasing inclination on the part of Southern Baptist Convention leaders to be more rigid on what is a Southern Baptist and exclusionary of accommodating those who differ from them." The New York Times called Carter's action "the highest-profile defection yet from the Southern Baptist Convention."
In subsequent years, Carter has joined with other world leaders who have spoken out about the subjugation of women by religious and other institutions. On July 15, 2009, Carter wrote an opinion piece about equality for women in which he stated that he chooses equality for women over the dictates of the leadership of what has been a lifetime religious commitment. He said that the view that women are inferior is not confined to one faith, "nor, tragically does its influence stop at the walls of the church, mosque, synagogue or temple." Carter stated:
The truth is that male religious leaders have had - and still have - an option to interpret holy teachings either to exalt or subjugate women. They have, for their own selfish ends, overwhelmingly chosen the latter. Their continuing choice provides the foundation or justification for much of the pervasive persecution and abuse of women throughout the world. This is in clear violation not just of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights but also the teachings of Jesus Christ, the Apostle Paul, Moses and the prophets, Muhammad, and founders of other great religions - all of whom have called for proper and equitable treatment of all the children of God. It is time we had the courage to challenge these views.[160]
Gun control
Carter has publicly expressed support for assault weapons bans and background checks.[161] In May of 1994, Carter, along with former presidents Gerald R. Ford and Ronald Reagan, wrote to the U.S. House of Representatives in support of banning "semi-automatic assault guns."[162] In a February 2013 appearance on Piers Morgan Tonight, Carter agreed that if the assault weapons ban did not pass it would be mainly due to the National Rifle Association and its pressure on "weak-kneed" politicians.[163]
Race in politics
Carter ignited debate in September 2009 when he stated, "I think an overwhelming portion of the intensely demonstrated animosity toward President Barack Obama is based on the fact that he is a black man, that he is African-American."[164][165] Obama disagreed with Carter's assessment. On CNN Obama stated, "Are there people out there who don't like me because of race? I'm sure there are ... that's not the overriding issue here."[166]
Torture
In a 2008 interview with Amnesty International, Carter criticized the alleged use of torture at Guantanamo Bay, saying that it "contravenes the basic principles on which this nation was founded."[167] He stated that the next President should publicly apologize upon his inauguration, and state that the United States will "never again torture prisoners."
Personal life

Carter and his wife, Rosalynn, are well known for their work as volunteers with Habitat for Humanity, a Georgia-based philanthropy that helps low-income working people around the world to build and buy their own homes and access clean water.
Carter's hobbies include painting,[168] fly-fishing, woodworking, cycling, tennis, and skiing.
Religion
From a young age, Carter showed a deep commitment to Christianity. He teaches Sunday school and is a deacon at the Maranatha Baptist Church in his hometown of Plains.[169][170][170] As president, Carter prayed several times a day, and professed that Jesus Christ was the driving force in his life. Carter had been greatly influenced by a sermon he had heard as a young man. It asked, "If you were arrested for being a Christian, would there be enough evidence to convict you?"[171] The New York Times noted that Carter had been instrumental in moving evangelical Christianity closer to the American mainstream during and after his presidency.[172]
In 2000, Carter severed his membership with the Southern Baptist Convention, saying the group's doctrines did not align with his Christian beliefs. In April 2006, Carter, former President Bill Clinton, and Mercer University President Bill Underwood initiated the New Baptist Covenant. The broadly inclusive movement seeks to unite Baptists of all races, cultures and convention affiliations. Eighteen Baptist leaders representing more than 20 million Baptists across North America backed the group as an alternative to the Southern Baptist Convention. The group held its first meeting in Atlanta, January 30 through February 1, 2008.[173]
Family
Carter had three younger siblings: sisters Gloria (1926–1990) and Ruth (1929–1983), and brother "Billy" (1937–1988). During Carter's presidency, Billy was often in the news, usually in an unflattering light.[174]
He is a first cousin of politician Hugh Carter. He is a half-second cousin of Motown founder Berry Gordy Jr. on his mother's side, and a cousin of June Carter Cash.[175]
He married Rosalynn Smith in 1946; they have three sons, one daughter, eight grandsons, three granddaughters, and two great-grandsons. They celebrated their 65th wedding anniversary in July 2011, making them the second-longest wed Presidential couple after George and Barbara Bush, a position they have held since passing John and Abigail Adams on July 10, 2000. Their eldest son Jack was the Democratic nominee for U.S. Senate in Nevada in 2006, losing to incumbent John Ensign. Jack's son Jason was elected to the Georgia State Senate in 2010.
Funeral and burial plans
Carter intends to be buried in front of his home in Plains, Georgia. Both President Carter and his wife Rosalynn were born in Plains. Carter also noted that a funeral in Washington, D.C. with visitation at the Carter Center is being planned as well.[176]
Honors and awards



Carter has received numerous awards and accolades since his presidency, and several institutions and locations have been named in his honor. His presidential library, Jimmy Carter Library and Museum was opened in 1986.[177] In 1998, the US Navy named the third and last Seawolf-class submarine honoring former President Carter and his service as a submariner officer. It became one of the first US Navy vessels to be named for a person living at the time of naming.[178] That year he also received the United Nations Human Rights Prize, given in honor of human rights achievements,[179] and the Hoover Medal, recognizing engineers who have contributed to global causes.[180] He won the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize,[181] which was partially a response to President George W. Bush's threats of war against Iraq and Carter's criticism of the Bush administration.[182] Six of Carter's audiobook recordings have been nominated for the Grammy Award for Best Spoken Word Album; his book Our Endangered Values won the award in 2007.[183][184] The Souther Field Airport in Americus was renamed Jimmy Carter Regional Airport in 2009.[185]
See also
- Electoral history of Jimmy Carter
- History of the United States (1964-1980)
- History of the United States (1980-1988)
- List of peace activists
- Jack Carter (politician) (born 1947; eldest son of former US President Jimmy Carter)
- Jason Carter (politician)
- Jimmy Carter rabbit incident
- "Mush From the Wimp" incident
- Raymond Lee Harvey assassination conspirator
Notes
- ^ Carter was the first future U.S. president to be born in a hospital.[6]
- ^ A popular anecdote holds that he was passed over for valedictorian after he and his friends skipped school to adventure downtown in a hot rod. The truancy was documented by a local newspaper, although it is not clear he would have been valedictorian otherwise.[7]
- ^ With Carter out of the race, Maddox narrowly won the runoff ballot over Arnall, clinching the Democratic nomination. In the general election, the Callaway won a plurality of the vote but came short of the 50 percent majority. The election was thus decided by the Georgia House of Representatives with its Democratic majority; they settled on Maddox.[25]
References
- ^ Warner, Greg. "Jimmy Carter says he can 'no longer be associated' with the SBC". Baptist Standard. Retrieved December 13, 2009.
He said he will remain a deacon and Sunday school teacher at Maranatha Baptist Church in Plains and support the church's recent decision to send half of its missions contributions to the Cooperative Baptist Fellowship.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter". New Georgia Encyclopedia. Georgia Humanities Council. Retrieved December 9, 2007.
- ^ "This Day in History – Iran Hostage Crisis ends". history.com. January 20, 1981. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ "Timeline and History of The Carter Center". The Carter Center. Retrieved February 16, 2010.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter and Habitat for Humanity". Habitat for Humanity Int'l.
- ^ a b c Bourne, pp. 11–32.
- ^ a b Bourne, pp. 33–43.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 44–55.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 72–77.
- ^ Frank, Northen Magill (1995). Great Events from History II: 1945–1966. p. 554.
- ^ Martel, Peter (2008). Memoirs of a Hayseed Physicist. p. 64.
- ^ Milnes, Arthur (January 28, 2009). "When Jimmy Carter faced radioactivity head-on". The Ottawa Citizen.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter - Biographical". Nobelprize.org. Retrieved November 29, 2013.
- ^ Paul Post (2010). Soldiers of Saratoga County: From Concord to Kabul. The History Press. pp. 105–. ISBN 978-1-59629-009-9.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 77–81.
- ^ Hayward, p. 23.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 83–91.
- ^ Morris, 115.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 92–108.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 108–132.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 132–140.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 132–145.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 145–149.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 149–153.
- ^ a b Bourne, pp. 153–165.
- ^ Bourne, 165–179.
- ^ Hayward, pp. 39–46.
- ^ a b c Bourne, 180–199.
- ^ a b Hayward, 46–51.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 200–201.
- ^ Hayward, pp. 49–55.
- ^ "TIME Magazine Cover: Gov. Jimmy Carter". Time. May 31, 1971. Retrieved July 8, 2014.
- ^ Bourne, p. 204.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 201–202.
- ^ a b Bourne, pp. 204–212.
- ^ Hayward, pp. 55–56.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 214–220.
- ^ a b Bourne, pp. 212–213.
- ^ a b Bourne, pp. 250–251.
- ^ Pilkington, Ed (November 11, 2013). "Jimmy Carter calls for fresh moratorium on death penalty". The Guardian.
- ^ Hugh S. Sidey (January 22, 2012). "Carter, Jimmy". World Book Student.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "World Book Encyclopedia (Hardcover) [Jimmy Carter entry]". World Book. January 2001. ISBN 0-7166-0101-X.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Associated Press (July 28, 2008). "Jimmy Carter battles plan for dams – again". NBCNews.com.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 213–214.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 221–230.
- ^ Bourne, pp. 237–250.
- ^ Mohr, Charles (July 16, 1976). "Choice of Mondale Helps To Reconcile the Liberals; Choice of Mondale as Running Mate Helps Carter to Reconcile Liberal Critics Candidate Tells of Painstaking Search In Effort to Avoid Mistake Like 1972's". The New York Times.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter". The American Experience. Public Broadcasting System.
- ^ "The Playboy Interview: Jimmy Carter." Robert Scheer. Playboy, November 1976, Vol. 23, Iss. 11, pp. 63–86.
- ^ Shoup (1980), The Carter Presidency and Beyond'
- ^ a b American Presidency, Brinkley and Dyer, 2004.
- ^ "Maine college to auction off former White House solar panels". October 28, 2004. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- ^ Burdick, Dave (January 27, 2009). "White House Solar Panels: What Ever Happened To Carter's Solar Thermal Water Heater? (VIDEO)". Huffington Post. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- ^ Philpott, Tom (August 17, 2011). "Beer Charts of the Day". Motherjones.com. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ "How Jimmy Carter Saved Craft Beer - Max Fisher". The Atlantic Wire. August 5, 2010. Retrieved September 18, 2013.
- ^ "Brewers Association". brewersassociation.org. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ^ Jimmy Carter (2005). Our Endangered Values: America's Moral Crisis. Simon and Schuster. p. 8.
- ^ Steven F. Hayward (2009). The Age of Reagan: The Fall of the Old Liberal Order: 1964–1980. Random House Digital, Inc. p. 497.
- ^ ""Nation: Kraft Drops Out", September 29, 1980". Time. September 29, 1980. Retrieved June 29, 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c "Jimmy Carter:39th president - 1977-1981". The Independent. London. January 22, 2009. Retrieved January 28, 2009.
- ^ "What History Foretells for Obama's First Job Approval Rating". Gallup.com. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ "Bush Presidency Closes With 34% Approval, 61% Disapproval". Gallup.com. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ "Polls: Ford's Image Improved Over Time". CBS News. December 27, 2006.
- ^ a b "Disaffection of the public - Jimmy Carter - election". Presidentprofiles.com. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ Dionne Jr, E. J. (May 18, 1989). "Washington Talk; Carter Begins to Shed Negative Public Image". The New York Times. Retrieved January 28, 2009.
- ^ "Time kind to former presidents, CNN poll finds". CNN. January 7, 2009.
- ^ Cinnamon Stillwell (December 12, 2006). "Jimmy Carter's Legacy of Failure". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter: Why He Failed – Brookings Institution". Brookings.edu. January 21, 2000. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ Ponnuru, Ramesh (May 28, 2008). "In Carter's Shadow". Time.
- ^ PBS Online/WGBH, "People & Events: Jimmy Carter's Post-Presidency", American Experience: Jimmy Carter, 1999–2001. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Brinkley, Douglas (Fall 1996). "The rising stock of Jimmy Carter: The 'hands on' legacy of our thirty-ninth President". Diplomatic History. 20 (4): 505–530. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7709.1996.tb00285.x.
- ^ Gibb, Lindsay (June 4, 2009). "Monte-Carlo TV fest opens with doc for first time". Retrieved June 12, 2012.
- ^ World Screen http://www.worldscreen.com/articles/display/21252
- ^ "Carter Center Guinea Worm Eradication Program - Dracunculiasis". The Carter Center. Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- ^ "Carter Center list of elections observed". The Carter Center. Retrieved April 30, 2014.
- ^ Norwegian Nobel Committee, 2002 Nobel Peace Prize announcement,[1], October 11, 2002. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Marion V. Creekmore, A Moment of Crisis: Jimmy Carter, The Power of a Peacemaker, and North Korea's Nuclear Ambitions (2006).
- ^ Fred Kaplan. "Rolling Blunder". Washington Monthly. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ James Brooke (September 5, 2003). "Carter Issues Warning on North Korea Standoff". The New York Times.
- ^ "Carter Issues Warning on North Korea Standoff"
- ^ Muravchik, Joshua (February 2007). "Our Worst Ex-President". Commentary. Retrieved July 5, 2008.
- ^ Justin McCurry (August 27, 2010). "North Korea releases US prisoner after talks with Jimmy Carter". The Guardian. London. Retrieved September 6, 2010.
- ^ BBC News Online, "Moderates launch Middle East plan", December 1, 2003. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Douglas G. Brinkley. The Unfinished Presidency: Jimmy Carter's Journey to the Nobel Peace Prize (1999), pp. 99–123.
- ^ Kenneth W. Stein, "My Problem with Jimmy Carter's Book", Middle East Quarterly 14.2 (Spring 2007).
- ^ "Israel 'has 150 nuclear weapons'". BBC News. May 26, 2008.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter Planning to meet Mashaal", The Jerusalem Post, April 9, 2008.
- ^ "PA to Carter: Don't meet with Mashaal." Associated Press. April 15, 2008.
- ^ "Carter: Rice did not advise against Hamas meeting." CNN. April 23, 2008.
- ^ Paris, Lebanon, and Syria Trip Report by Former US President Jimmy Carter: December 5–16, 2008 The Carter Center, December 18, 2008.
- ^ Jimmy Carter says Israel had 150 nuclear weapons, The Times.
- ^ "PR-USA.net". PR-USA.net. November 1, 2007. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ Jimmy Carter speaks to Forward Magazine[dead link].
- ^ Erick Stakelbeck (March 24, 2011). "Int'l Red Cross Sheltering Hamas Terrorist Officials". Cbn.com. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ Press Release, African Leaders Gather to Address Great Lakes Crisis, May 2, 1996. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ The Nairobi Agreement, December 8, 1999. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Larry Rohter, "Showdown with Haiti: Diplomacy; Carter, in Haiti, pursues peaceful shift", The New York Times, September 18, 1994. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Carter Center News, July–December 2002. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ BBC News, Lift Cuba embargo, Carter tells US, May 15, 2002. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Jose De Cordoba, and David Luhnow, "Venezuelans Rush to Vote on Chávez: Polarized Nation Decides Whether to Recall President After Years of Political Rifts", The Wall Street Journal (Eastern edition), New York City, August 16, 2004, p. A11.
- ^ "Venezuelan Audit Confirms Victory", BBC News, September 21, 2004. Retrieved November 5, 2005.
- ^ Carter Center (2005). Observing the Venezuela Presidential Recall Referendum: Comprehensive Report. Retrieved January 25, 2006.
- ^ Newman, Lucia (August 17, 2004). "Winner Chavez offers olive branch". CNN. Retrieved July 5, 2008.
- ^ M. Barone, "Exit polls in Venezuela," US News & World Report, August 20, 2004.
- ^ "US Poll Firm in Hot Water in Venezuela". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on August 20, 2004. Retrieved November 29, 2010.
- ^ "Ecuador and Colombia Presidents Accept President Carter's Proposal to Renew Diplomatic Relations at the Level of Chargé d'Affaires, Immediately and Without Preconditions" (Press release). The Carter Center. June 8, 2008. Retrieved June 8, 2008.
- ^ "Colombia, Ecuador restore ties under deal with Carter". Thomson Reuters. June 8, 2008. Retrieved June 8, 2008.
- ^ Cựu Tổng thống Mỹ Jimmy Carter đến Việt Nam Template:Vi
- ^ "What is The Elders?". The Elders. Retrieved March 8, 2013.
- ^ "Our Work". The Elders. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter". The Elders. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter blocked from meeting Darfur chief". Reuters. October 3, 2007. Retrieved June 12, 2012.
- ^ Ian Timberlake (May 27, 2012). "Sudan ready to withdraw troops from Abyei: Jimmy Carter". AFP. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter and Lakhdar Brahimi in Sudan to support peace efforts". The Elders. May 27, 2012. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- ^ "Annan, Carter say barred from Zimbabwe". Reuters. November 22, 2008. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- ^ "Carter slams Clinton pardon". CNN. February 21, 2001. Archived from the original on May 17, 2008. Retrieved July 5, 2008.
- ^ Jimmy Carter, "Just War -- or a Just War?", The New York Times, March 9, 2003. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter: Blair Subservient to Bush". The Washington Post. Associated Press. August 27, 2006. Retrieved July 5, 2008.
- ^ Frank Lockwood, "Carter calls Bush administration worst ever", Arkansas Democrat-Gazette, May 19, 2007. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter Can Only Blame Himself", American Thinker, May 25, 2007.
- ^ "Carter: Anti-Bush remarks 'careless or misinterpreted'", Associated Press, May 21, 2007. Retrieved May 21, 2007.
- ^ "'Carter is irrelevant,' Bush administration shoots back[dead link]", Associated Press, May 20, 2007. Retrieved May 21, 2007. Archived by the Wayback Machine beta.
- ^ a b "Carter attacks Blair's Iraq role". BBC News. May 19, 2007. Retrieved July 5, 2008.
- ^ Associated Press, "Carter says US should close detention center at Guantanamo", June 8, 2005. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Newsnight audio recording, September 2006, BBC.
- ^ Jimmy Carter Speaks to Forward Magazine.[dead link]
- ^ "Jimmy Carter Speaks to Forward Magazine". January 2009. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- ^ "Americas – US 'likely behind' Chavez coup". Al Jazeera English. September 21, 2009. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ Carter, Jimmy (June 16, 2011). "Call Off the Global Drug War". The New York Times.
- ^ Bingham, Amy (June 25, 2012). "Jimmy Carter Accuses U.S. of 'Widespread Abuse of Human Rights'". ABC News. Retrieved June 26, 2012. ABC quotes came from a NY Times June 25, 2012 op-ed written by Carter
- ^ Greg Bluestein, Jim Galloway (July 18, 2013). "Your daily jolt: 'America has no functioning democracy,' says Jimmy Carter". Atlanta Journal Constitution. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- ^ Peter Schmitz (July 17, 2013). "NSA-Affäre: Ex-Präsident Carter verdammt US-Schnüffelei". Der Spiegel. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- ^ Remarks by Former U.S. President Jimmy Carter at Brandeis University, The Carter Center, January 23, 2007. Retrieved September 19, 2010.
- ^ a b "Simon & Schuster: Palestine Peace Not Apartheid (Hardcover) – Read an Excerpt,", Simon & Schuster, November 2006. Retrieved April 9, 2007.
- ^ Speaking Frankly about Israel and Palestine, Los Angeles Times, December 8, 2006, Op-Ed. Retrieved January 4, 2007.
- ^ Dennis Ross, "Don't Play With Maps," The New York Times, January 9, 2007. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ^ Kenneth W. Stein, "My Problem with Jimmy Carter's Book," Middle East Forum, Spring, 2007. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ^ Julie Bosman, "Carter Book Stirs Furor With Its View of Israelis' 'Apartheid'" The New York Times, December 14, 2006. Retrieved March 29, 2008.
- ^ Alan Dershowitz (November 22, 2006). "The World According to Carter". The New York Sun. Retrieved September 25, 2007.
- ^ Sony Classics Pictures, Jimmy Carter: Man from Plains[dead link]. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ "Ex-President Carter offers apology to Jews". Associated Press. December 23, 2009. Retrieved October 18, 2011.
- ^ "16 – BCCI And Georgia Politicians". Fas.org. Retrieved September 6, 2010.
- ^ "Could Jimmy Carter's Comments Doom Mitt Romney?". The International Business Times Inc. Retrieved September 22, 2011.
- ^ Yahoo News, Jimmy Carter wants Mitt Romney to be the Republican nominee, September 16, 2011. Retrieved October 5, 2011.
- ^ Camia, Catalina (August 7, 2012). "Jimmy Carter to speak by video at Dem convention". USA TODAY. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- ^ "Honorary Chairs". World Justice Project. Retrieved February 24, 2010.
- ^ "About the Opportunity Fund". World Justice Project. Retrieved February 24, 2010.
- ^ John-Henry Westen (November 7, 2005). "Jimmy Carter Using Abortion to Split Support for Republicans?". LifeSiteNews.com.
- ^ Skinner, Kudelia, Mesquita, Rice (2007). The Strategy of Campaigning. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-11627-0. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Carter: Jesus Would Not Approve of Abortions", CBS Atlanta, March 30, 2012. Retrieved March 30, 2012
- ^ Jimmy Carter: Democratic Party Should Be More Pro-Life, March 29, 2012
- ^ "Democrats shift on death penalty", Boston Globe, December 7, 2003
- ^ "Carter Nobel Peace Prize speech", CNN, December 10, 2002
- ^ "NEW VOICES: Jimmy Carter Urges New Mexico Governor to Support Death Penalty Repeal | Death Penalty Information Center". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ Carter, Jimmy, "Jimmy Carter to California: Yes on Prop. 34" (op-ed), LA Times, October 28, 2012. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
- ^ "Brian Baldwin, Center on Wrongful Convictions". Law.northwestern.edu. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ "Jimmy Carter, Desmond Tutu Urge Texas to Stay Execution of Kenneth Foster". Democracynow.org. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ "Clemency | Death Penalty Information Center". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ The Carter Center (September 19, 2008). "Carter Center Press Releases – President Carter Calls for Clemency for Troy Davis". The Carter Center. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ Losing my religion for equality, Opinion, Theage.com.au, July 15, 2009
- ^ Carter, Jimmy (April 26, 2009). "What Happened to the Ban on Assault Weapons?". New York Times (Op-ed). Retrieved July 4, 2014.
- ^ Eaton, William J. (May 5, 1994). "Ford, Carter, Reagan Push for Gun Ban". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved July 4, 2014.
- ^ Kurtz, Jason (February 22, 2013). "Clips From Last Night: Jimmy Carter on firearm legislation, the NRA, and the conflict in the Middle East". Cable News Network. Retrieved July 4, 2014.
- ^ "NBC Nightly News with Brian Williams: News and videos from the evening broadcast NBC Nightly News with Brian Williams: News and videos from the evening broadcast". MSNBC. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ "White House disputes Carter's analysis - Capitol Hill". MSNBC. September 16, 2009. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ O'Brien, Michael (September 19, 2009). "Obama plays down role of race in criticism – The Hill's Blog Briefing Room". Thehill.com. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ Torture can never be justified on YouTube
- ^ Carter, Jimmy, Letter to Artist Mia LaBerge, February 14, 2008.
- ^ Somini Sengupta, "Carter Sadly Turns Back on National Baptist Body", The New York Times, October 21, 2000. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ a b Maranatha Baptist Church. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Carter, Jimmy; Richardson, Don (1998). Conversations with Carter. Lynne Rienner Publishers. p. 14. ISBN 1-55587-801-6.
- ^ Sengupta, S. (October 21, 2000). Carter Sadly Turns Back On National Baptist Body. The New York Times. Retrieved on: March 31, 2013.
- ^ New Baptist Covenant. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ Robert D. Hershey Jr (September 26, 1988). "Billy Carter Dies of Cancer at 51; Troubled Brother of a President". The New York Times. Retrieved July 27, 2011.
- ^ Cash, John R. with Patrick Carr (1997). Johnny Cash, the Autobiography. Harper Collins.
- ^ Associated Press, "President Carter Talks of Funeral Plans", December 3, 2006. Retrieved October 13, 2009.
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/1993/05/30/travel/carter-center-more-than-the-past.html?pagewanted=all
- ^ Jamie McIntyre, "Navy to name submarine after former President Jimmy Carter", CNN, April 8, 1998. Retrieved August 4, 2008.
- ^ http://www.ohchr.org/EN/NewsEvents/Pages/HRPrizeListofpreviousrecipients.aspx
- ^ https://www.asme.org/about-asme/get-involved/honors-awards/unit-awards/hoover-awards/1998
- ^ http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/2002/press.html
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20021016213347/http://www.cnn.com/2002/WORLD/europe/10/11/carter.nobel/index.html
- ^ http://dailycaller.com/2013/02/11/the-liberal-history-of-the-grammys-spoken-word-category/
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/2007/02/12/arts/music/12gram.html?_r=0
- ^ http://www.foxnews.com/politics/2009/10/11/jimmy-carter-regional-airport-reality/
Further reading
- Allen, Gary. Jimmy Carter, Jimmy Carter, '76 Press, 1976.
- Berggren, D. Jason and Rae, Nicol C. "Jimmy Carter and George W. Bush: Faith, Foreign Policy, and an Evangelical Presidential Style." Presidential Studies Quarterly 2006 36(4): 606–632. ISSN 0360-4918
- Busch, Andrew E. Reagan's Victory: The Presidential Election of 1980 and the Rise of the Right, (2005) online review by Michael Barone
- Freedman, Robert. "The Religious Right and the Carter Administration." Historical Journal 2005 48(1): 231–260. ISSN 0018-246X
- Godbold, Jr., E. Stanly. Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter: The Georgia Years, 1924–1974 354 pages (Oxford University Press; 2010)
- The New York Times "Topics; Thermostatic Legacy", January 1, 1981, Section 1, Page 18, Column 1
- Harris, David (2004). The Crisis: the President, the Prophet, and the Shah—1979 and the Coming of Militant Islam. Little, Brown.
- Regarding the failed Iranian mission to rescue the American hostages
- Bourne, Peter G. (1997). Jimmy Carter: A Comprehensive Biography From Plains to Post-Presidency. New York: Scribner. ISBN 0-684-19543-7.
- Clymer, Kenton. "Jimmy Carter, Human Rights, and Cambodia." Diplomatic History 2003 27(2): 245–278. ISSN 0145-2096
- Dumbrell, John (1995). The Carter Presidency: A Re-evaluation (2nd ed.). Manchester: Manchester University Press. ISBN 0-7190-4693-9.
- Fink, Gary M. (1998). The Carter Presidency: Policy Choices in the Post-New Deal Era. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0-7006-0895-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Flint, Andrew R.; Joy Porter (March 2005). "Jimmy Carter: The re-emergence of faith-based politics and the abortion rights issue". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 35 (1): 28–51. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5705.2004.00234.x.
- Gillon, Steven M. (1992). The Democrats' Dilemma: Walter F. Mondale and the Liberal Legacy. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-07630-4.
- Glad, Betty (1980). Jimmy Carter: In Search of the Great White House. New York: W. W. Norton. ISBN 0-393-07527-3.
- Hahn, Dan F. (1992). "The rhetoric of Jimmy Carter, 1976–1980". In in Theodore Windt and Beth Ingold (ed.). Essays in Presidential Rhetoric (3rd ed.). Dubuque, Iowa: Kendall/Hunt. pp. 331–365. ISBN 0-8403-7568-9.
- Hargrove, Erwin C. (1988). Jimmy Carter as President: Leadership and the Politics of the Public Good. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-1499-5.
- Hayward, Steven F. (2004). The Real Jimmy Carter: How Our Worst Ex-President Undermines American Foreign Policy, Coddles Dictators and Created the Par. Regnery Publishing. ISBN 978-1-59698-278-9.
- Jones, Charles O. (1988). The Trusteeship Presidency: Jimmy Carter and the United States Congress. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-1426-X.
- Jorden, William J. (1984). Panama Odyssey. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-76469-3.
- Kaufman, Burton I. (1993). The Presidency of James Earl Carter, Jr. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0-7006-0572-X.
- Kucharsky, David (1976). The Man From Plains: The Mind and Spirit of Jimmy Carter. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 0-06-064891-0.
- Mattson, Kevin, with a foreword by Hendrik Hertzberg "'What the Heck Are You Up To, Mr. President?'", Bloomsbury USA, 2010.
- Morgan, Iwan. "Jimmy Carter, Bill Clinton, and the New Democratic Economics." Historical Journal 2004 47(4): 1015–1039. ISSN 0018-246X
- Morris, Kenneth Earl. Jimmy Carter, American Moralist. University of Georgia Press year=1996.
{{cite book}}: Missing pipe in:|publisher=(help) - Ribuffo, Leo P. (1989). "God and Jimmy Carter". In M. L. Bradbury and James B. Gilbert (ed.). Transforming Faith: The Sacred and Secular in Modern American History. New York: Greenwood Press. pp. 141–159. ISBN 0-313-25707-8.
- Ribuffo, Leo P. (1997). "'Malaise' revisited: Jimmy Carter and the crisis of confidence". In John Patrick Diggins (ed.) (ed.). The Liberal Persuasion: Arthur Schlesinger, Jr. and the Challenge of the American Past. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 164–185. ISBN 0-691-04829-0.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help) - Rosenbaum, Herbert D. (1994). The Presidency and Domestic Policies of Jimmy Carter. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. pp. 83–116. ISBN 0-313-28845-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Schram, Martin (1977). Running for President, 1976: The Carter Campaign. New York: Stein and Day. ISBN 0-8128-2245-5.
- Schmitz, David F. and Walker, Vanessa. "Jimmy Carter and the Foreign Policy of Human Rights: the Development of a Post-cold War Foreign Policy." Diplomatic History 2004 28(1): 113–143. ISSN 0145-2096
- Strong, Robert A. (Fall 1986). "Recapturing leadership: The Carter administration and the crisis of confidence". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 16 (3): 636–650.
- Strong, Robert A. (2000). Working in the World: Jimmy Carter and the Making of American Foreign Policy. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-2445-1.
- White, Theodore H. (1982). America in Search of Itself: The Making of the President, 1956–1980. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 0-06-039007-7.
- Witcover, Jules (1977). Marathon: The Pursuit of the Presidency, 1972–1976. New York: Viking Press. ISBN 0-670-45461-3.
Primary sources
- Califano, Joseph A., Jr. Governing America: An insider's report from the White House and the Cabinet. 1981
- Jordan, Hamilton. Crisis: The Last Year of the Carter Presidency. 1982
- Lance, Bert. The Truth of the Matter: My Life in and out of Politics. 1991
External links
- Jimmy Carter Library and Museum
- The Carter Center: Advancing Human Rights and Alleviating Suffering
- Oral History Interview with Jimmy Carter from Oral Histories of the American South
- Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter Partnership Foundation
- Text and Audio of Carter's Crisis of Confidence (Malaise) Speech
- Text and Notes to Carter's Undelivered Energy Speech
- Interpretive essay in New Georgia Encyclopedia
- Website about Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter
- Jimmy Carter's Visit to Cuba – May 12–17, 2002
- Wit and Wisdom of Jimmy Carter – slideshow by Life magazine (archived link)
- Extensive collection of Oral History Transcripts on the Carter Administration from the Miller Center of Public Affairs (UVa)
- Oral History Interview with President Jimmy Carter, May 4, 1993 Georgia's Political Heritage Program, Digital Library of Georgia
- Extensive essay on Jimmy Carter and shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady from the Miller Center of Public Affairs
- Jimmy Carter at C-SPAN's American Presidents: Life Portraits
- In Depth interview with Carter, December 3, 2006
- PBS's "American Experience" - The Presidents: Jimmy Carter
Biographical pages
- "James Carter". The White House.
- "Jimmy Carter". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- "Jimmy Carter". Our Georgia History.
- President James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. "Submariner". Submarine History.
Other links
- War and Peace in the Nuclear Age
- Inaugural Address of Jimmy Carter via re-quest.net
- State of the Union Addresses: 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981 (written message) at UCSB's American Presidency Project
- Nobel lecture, Oslo, Norway (December 10, 2002)
- About the malaise speech, via PBS
- The 1980 October Surprise
- "The US President was here" – about Carterpuri, a village in Haryana, India named after President Carter
- Instruments of Statecraft: US Guerrilla Warfare, Counterinsurgency, and Counterterrorism, 1940–1990 Chap. 3 The Carter Years
- Korea Society Podcast: A Moment of Crisis: Jimmy Carter's 1994 Mission to Pyongyang
- Works by Jimmy Carter at Project Gutenberg
- Jimmy Carter's thoughts on Earth Day 2006
- Jimmy Carter's op/ed commentaries for Project Syndicate
- Interview with Jimmy Carter (August 2006)
- Interview with Jimmy Carter on Current Campaign (April 2007)
- Interview with Jimmy Carter (April 2007) on Speaking of Faith with Krista Tippett
- Jimmy Carter on The Hour with George Stroumboulopoulos
- All articles with faulty authority control information
- Jimmy Carter
- 1924 births
- Living people
- American democracy activists
- American diplomats
- American farmers
- American gun control advocates
- American humanitarians
- American memoirists
- American military personnel of World War II
- American Nobel laureates
- 21st-century American novelists
- American people of English descent
- American people of Scotch-Irish descent
- American political writers
- Baptists from the United States
- Cold War leaders
- Democratic Party Presidents of the United States
- Democratic Party state governors of the United States
- Emory University faculty
- Georgia Institute of Technology alumni
- Georgia Southwestern State University alumni
- Georgia (U.S. state) Democrats
- Georgia (U.S. state) State Senators
- Governors of Georgia (U.S. state)
- Grammy Award-winning artists
- Grand Crosses of the Order of Vasco Núñez de Balboa
- History of the United States (1964–80)
- Nobel Peace Prize laureates
- People from Plains, Georgia
- People of the Soviet war in Afghanistan
- Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients
- Presidents of the United States
- Recipients of the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
- Sons of the American Revolution
- Submariners
- Union College (New York) alumni
- United States Naval Academy alumni
- United States Navy officers
- United States presidential candidates, 1976
- United States presidential candidates, 1980
- Writers from Georgia (U.S. state)
